Digital smile design (DSD) is a cutting-edge method for analysing, organising, and producing aesthetically beautiful smiles, commonly referred to as smile design dentistry. Digital smile design involves the use of imaging software, intraoral scanning, and virtual simulations to design the desired smile.
Dentists personalise treatment regimens, interact with patients graphically, and guarantee a more consistent result with DSD. Improved visualisation, exact planning, better communication, and higher patient satisfaction are all benefits of DSD.
There are other factors to take into account like the price of deploying digital technology, the learning curve related to employing DSD tools, and the potential limits of digital simulations in comparison to actual results. DSD is a cutting-edge and successful method for developing beautiful smiles with individualised treatment programmes and increased patient engagement.
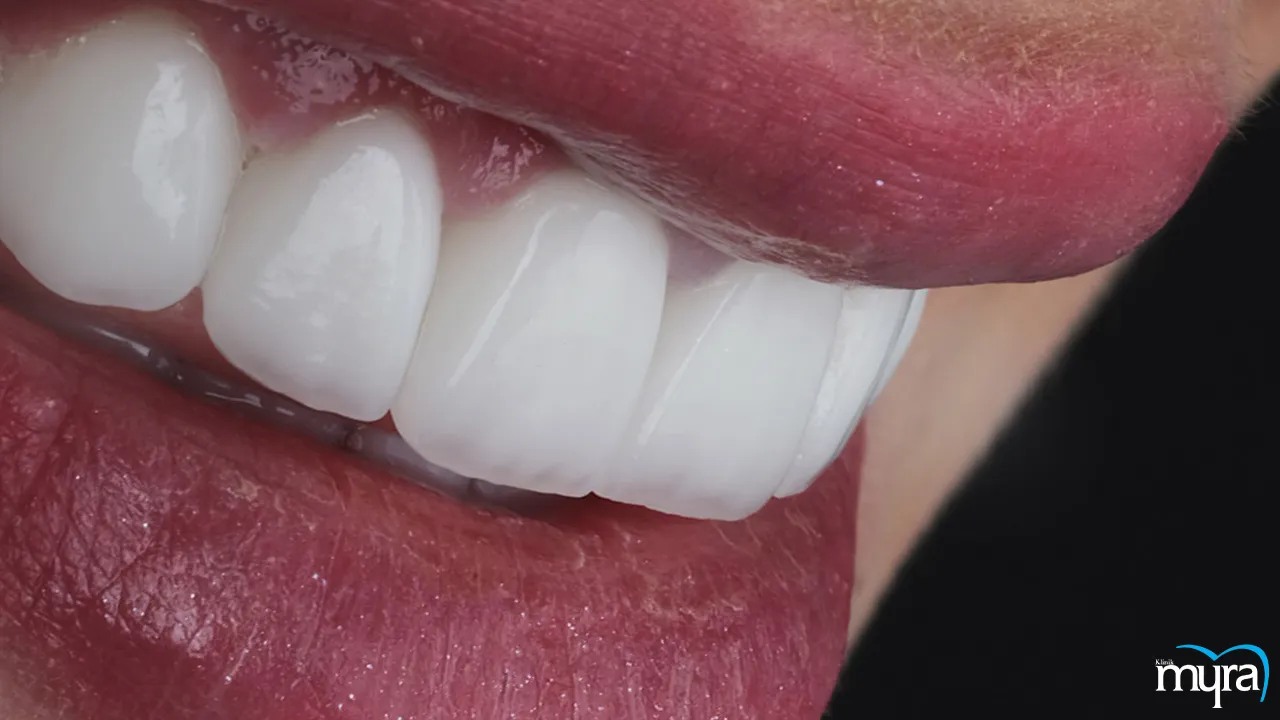
What is Digital Smile Design?
Digital Smile Design (DSD) is a concept and treatment planning technique in dentistry that combines aesthetics, dentistry, and digital technology. Digital Smile Design involves using advanced digital imaging and software to develop a virtual model of a patient's smile, allowing dentists to visualise and plan the desired outcome.
DSD enhances communication between patients and dentists, improves treatment predictability, and offers a personalised approach to smile design. It has revolutionised aesthetic and restorative dentistry by leveraging digital technology for precise planning and optimal aesthetic results.
How Digital Smile Design Works?
Listed below are the steps on how Digital Smile Design works.
- An initial consultation is the first step. The procedure begins with an initial consultation between the patient and the dentist. The patient expresses their concerns, hopes, and aspirations for their smile.
- A comprehensive examination is the second step. The dentist examines the patient's oral health in detail, including the teeth, gums, bite, and general face attractiveness. Existing dental problems, like decay or misalignment, are recognised and treated.
- Digital imaging is the third step. High-quality images, videos, and digital scans of the patient's face, teeth, and smile are taken using specialist imaging equipment. These photographs are used to kick off the digital grin design process.
- Smile analysis is the fourth step. The dentist examines the patient's facial features, tooth shape, colour, symmetry, and smile aesthetics. They take into account a variety of elements, including the patient's gender, age, personality, and cultural background, to produce a smile design that is unique to the individual.
- Facial and Tooth Design is the fifth step. The dentist manipulates digital photos with specialist software to create the desired alterations to the patient's smile. They change the shape, size, position, and colour of teeth to get the desired cosmetic result.
- Virtual Mock-up is the sixth step. A virtual mock-up is built based on the digital smile design. It is accomplished by superimposing the planned alterations onto the patient's original pictures, resulting in a visual representation of how the new smile seems. The patient observes and assesses the probable outcomes.
- Treatment planning is the seventh step. The virtual mock-up is used as a guide by the dentist to construct a comprehensive treatment plan. The plan includes operations such as tooth whitening, veneers, crowns, orthodontics, or dental implants, depending on the patient's demands.
- Communication and Collaboration are the eight steps. The digital smile design acts as a tool for communication between the dentist, dental laboratory, and other dental professionals participating in the treatment. It enables the transmission of clear and precise instructions, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding the desired objectives.
- Implementation is the ninth step. The appropriate dental treatments are carried out to bring the digital smile design to life following the approval of the treatment plan. It includes tooth preparation, restoration manufacturing, orthodontic alignment, gum contouring, and other aesthetic or restorative treatments.
- Evaluation and Maintenance is the last step. The dentist reviews the final results to verify they are consistent with the digital smile design following treatment completion. Any essential changes or improvements are made. The patient is advised on how to maintain and care for the new smile in the long run.
1. Initial Consultation
The dentist begins the Initial Consultation step of Digital Smile Design by interviewing the patient to learn about their dental history, concerns, and desired objectives. The conversation allows the dentist to identify any specific concerns with the patient's smile, such as tooth discolouration, misalignment, or gaps.
The dentist then does a facial examination, thoroughly inspecting the patient's facial features. They consider criteria such as facial form, lip dynamics, and facial symmetry. The analysis aids in determining how the grin must complement the appearance of the patient's face.
The dentist evaluates the patient's current smile, looking at tooth alignment, colour, form, and other characteristics. The evaluation allows them to discover areas that need to be improved and leads to the subsequent treatment planning procedure.
High-quality digital photos of the patient's face, teeth, and smile are captured using specialist imaging equipment to create a full record of their smile. Assisting in proper analysis and communication during the design and planning stages, these photographs serve as visual references for the dentist.
The dentist documents the patient's dental and medical history during the Initial Consultation, including any existing dental issues, previous treatments, and relevant health information. The documentation ensures a thorough grasp of the patient's history and aids in developing a specific treatment plan.
2. Comprehensive Examination
The dentist evaluates the patient's oral health and facial attractiveness in depth during the Comprehensive Examination step of Digital Smile Design. The dentist does an oral health assessment, which includes an examination of the patient's teeth, gums, and oral condition. They examine the teeth for decay, gum disease, and the existence of any dental restorations or prostheses.
The patient's teeth and supporting structures are then captured in detail using modern digital imaging techniques such as intraoral scanners or X-rays. These scans provide important information about the state of the teeth and aid in the identification of any underlying dental disorders.
The dentist examines the patient's bite, determining how the upper and lower teeth fit together when the jaws are closed. The bite analysis aids in the identification of any accusal abnormalities that have an impact on the aesthetics and functionality of the smile.
The dentist does a face examination following the initial session. They look at things like facial symmetry, profile, and soft tissue aesthetics to see how the smile affects the harmony of the face.
An aesthetic evaluation is performed, in which the dentist evaluates several aesthetic elements such as tooth shape, colour, size, and proportion. They consider the patient's preferences, gender, age, and distinctive qualities to create a smile design that complements their unique features.
The dentist assesses the functionality of the patient's bite and jaw movements. They examine how the teeth and jaws interact during activities such as chewing and speaking to ensure that the recommended treatment plan takes into account both aesthetic and functional concerns.
The dentist acquires a plethora of information regarding the patient's oral health, dental structure, face aesthetics, and functional elements by doing a complete examination. A thorough understanding serves as the foundation for designing an effective treatment plan that is in line with the patient's desired smile outcomes and oral health.
3. Digital Imaging
Advanced imaging technologies are used to capture high-quality digital photographs of the patient's face, teeth, and smile during the Digital Imaging portion of Digital Smile Design. These visuals serve as a critical foundation for the process's following design and planning stages.
The dentist uses an intraoral scanner to acquire digital impressions of the patient's teeth and oral tissues. The handheld device makes a precise 3D model of the patient's dentition using optical technologies. It does away with the need for untidy impression materials and offers accurate digital data.
High-resolution digital photos of the patient's face from various angles are obtained, aside from intraoral scanning. These photographs depict the entire appearance of the face, including the lips, gums, and surrounding tissues. They are useful for grin design and analysis.
Smile portraits are images that are taken specifically to focus on the patient's smile. The dentist directs the patient to naturally pose and grin, obtaining images that depict the current state of the teeth, gingiva, and lip dynamics. These grin portraits are useful in evaluating aesthetics and planning the desired smile outcome.
Full-face photos are obtained to assess facial harmony and how the grin interacts with other facial features. These photographs provide a thorough insight into the patient's aesthetics and serve as a reference for the smile design process.
Images of the patient's teeth and underlying bone anatomy are captured if X-rays or other radiographic imaging techniques are judged required. These scans provide essential diagnostic information about dental health, root placements, bone levels, and potentially apparent abnormalities.
All digital photos are integrated into specialist software, including intraoral scans, extra-oral photographs, grin portraits, and radiographic images. The dentist now has a complete digital record of the patient's oral condition, facial features, and smile characteristics because of the connection.
The dentist obtains an accurate and detailed representation of the patient's teeth and facial anatomy by using digital imaging techniques. These digital data form the foundation for additional analysis, smile design, and treatment planning, allowing for a more accurate and efficient approach to obtaining the desired smile makeover or dental repair.
4. Smile Analysis
The dentist undertakes a detailed study of many aspects of the patient's smile during the Smile Analysis step of Digital Smile Design to assess its current state and establish the desired aesthetic goals. The study forms the foundation for the succeeding stages of smile design and treatment planning.
The dentist starts by examining the teeth, looking at things like colour, shape, size, position, and alignment. They discover any dental abnormalities that affect the looks of the smile, such as discolouration, chipped tooth or damaged teeth, gaps, or misalignment.
The dentist then examines the patient's gums to determine their health and look. They assess the gum line's form, symmetry, and the quantity of gum tissue visible when smiling. The evaluation determines whether any gum reshaping or gum contouring is required to improve the smile's aesthetics.
The dentist looks at the patient's lips in connection to their grin. Lip dynamics, fullness, symmetry, and the way the lips frame the teeth when smiling are all taken into account. The study contributes to the design of a grin that complements the patient's natural lip and facial expressions.
The dentist assesses the patient's facial features and facial harmony. Facial form, symmetry, and dimensions are all considered, ensuring that the proposed smile matches and enhances the patient's facial aesthetics.
The dentist examines the smile line, which is the imaginary line formed by the upper teeth's edges when smiling. The symmetry, alignment, and visibility of the teeth within the smile line are evaluated to see whether any changes are required for a balanced and aesthetically acceptable smile.
The dentist converses with the patient to learn about their particular preferences and expectations for their smile makeover during the Smile Analysis. It includes taking into account the patient's desires, cultural background, and individual traits to produce a smile design that aligns with their specific aesthetic goals.
The dentist acquires a full grasp of the patient's current smile and intended results by doing a comprehensive Smile Analysis. The analysis directs the subsequent smile design and treatment planning process, ensuring that the planned adjustments result in a beautiful, natural-looking grin that complements the patient's facial features and personal preferences.
5. Facial and Tooth Design
The dentist uses sophisticated software and digital tools to design the desired aesthetic outcomes for the patient's facial features and teeth during the Facial and Tooth Design step of Digital Smile Design. The process entails a thorough examination and alteration of many elements to produce a unique grin design.
The dentist examines the patient's existing teeth to determine their shape and size. They determine the optimal tooth shape and size for the desired outcome by taking into account aspects such as gender, age, facial features, and individual preferences. It guarantees that the patient's entire appearance is enhanced by the smile design.
The dentist concentrates on tooth position and alignment. They use digital tools to make modifications to improve symmetry and general appearance. Minor adjustments are required to rectify misalignments, narrow gaps, or produce a more harmonious smile.
The examination involves an assessment of tooth colour and tone. The dentist evaluates the colour of the patient's natural teeth and takes into account any desired alterations. They experiment with several shades using digital simulations to identify the best colour for restorations or improvements.
Gum contouring is another critical part of the design process. The dentist examines the patient's gum line attentively and changes to get an optimum gum contour that complements the smile design. It entails reshaping or re-contouring the gums to produce a balanced and aesthetically acceptable framing for the teeth.
The dentist ensures that the planned tooth design complements the patient's lips and other facial features throughout the process. Lip dynamics, facial symmetry, and facial profile are all taken into account while designing a smile to suit the patient's particular facial aesthetics.
A virtual mock-up is made using specialist software to visualise the proposed alterations. The necessary changes are digitally superimposed onto the patient's current dental and facial photographs by the dentist. It enables the patient to envision the possible outcome and actively engage in the design process by providing input.
The dentist adjusts many parts of the teeth and facial features using computerised equipment and software to produce a unique smile design. The holistic method takes into account tooth shape, size, alignment, colour, gum contouring, and face harmony. The virtual prototype encourages collaboration between the dentist and the patient, ensuring that the final smile design satisfies the patient's aesthetic and expectations.
6. Virtual Mockup
The dentist uses specialised software to produce a digital representation of the suggested smile design during the Virtual Mock-up portion of the Digital Smile Design. Several critical elements are included in the process to enable an accurate depiction of the required modifications.
The dentist utilises specialist software to design the required smile changes based on an analysis of the patient's facial traits and dental characteristics. It includes changes to the shape, size, position, alignment, and colour of the teeth. The software includes capabilities for manipulating digital photos and creating a personalised grin design that meets the patient's aesthetic goals.
The dentist enters the program with the digital records obtained during the initial consultation and imaging stages. Intraoral scans, extra-oral pictures, grin portraits, and other pertinent images are included. The dentist generates a thorough digital dataset by merging information, which acts as a reference for the virtual mock-up.
The dentist superimposes the suggested modifications over the patient's current dental and facial pictures using sophisticated software. It entails superimposing the digital grin design over the existing teeth, gums, and facial characteristics. The result is a graphic picture of how the new grin seems concerning the patient's distinct facial features.
The virtual simulation allows the patient to see and assess the prospective outcome of the smile makeover. The digitised images are displayed on a computer screen or other visualisation tools by the dentist, providing a realistic glimpse of the recommended alterations. The representation assists the patient in comprehending the expected outcomes and actively participating in the decision-making process.
The patient's feedback is an important element of the virtual mock-up process. The patient has the opportunity to voice their choices, discuss any concerns, and provide comments on the suggested design. The dentist considers feedback and makes further changes to the smile design to ensure that it meets the patient's expectations and aesthetic goals.
The dentist creates a complete treatment plan based on the virtual simulation. The computerised image is used as a guide to determine the methods and materials needed to create the desired smile design. It makes it easier to communicate and collaborate with other dental professionals engaged in the treatment procedure.
The Virtual Mock-up stage improves communication between the dentist and the patient, enabling a collaborative approach. It allows the patient to visualise proposed changes, provide input, and actively participate in decision-making. The dentist guarantees that the final result matches the patient's expectations and intended smile design by using the virtual mock-up as a template.
7. Treatment Planning
The dentist creates a complete plan based on the digital records, virtual mock-up, and patient input during the Treatment Planning portion of Digital Smile Design. The step entails thorough consideration of the desired smile design as well as the methods required to obtain the desired results.
The dentist begins by going over the digital records gathered during the first consultation, detailed examination, and virtual mock-up stages extensively. Intraoral scans, extra-oral pictures, grin portraiture, radiographic images, and the virtual mock-up are all included. The dentist acquires a full grasp of the patient's dental condition, facial features, and proposed smile design by studying these records.
The proposed smile design is validated based on the patient's feedback, preferences, and desired goals. The dentist makes certain that the design corresponds to the patient's aesthetic desires and facial harmony. Any necessary tweaks or refinements to the smile design are made.
The dentist then determines the specific dental operations needed to attain the desired results. Treatments such as tooth whitening, veneers, crowns, orthodontics, dental implants, or gum contouring are included. The dentist takes into account the patient's dental health, functional needs, and expected cosmetic results when deciding on treatments.
Procedures are carefully sequenced to maximise treatment efficiency and patient comfort. The dentist takes into account aspects such as the necessity for any preliminary treatments, the incorporation of orthodontics if necessary, and the best scheduling for each stage. The sequencing guarantees that the intended smile alteration is achieved systematically.
Digital Smile Design makes it easier for the dentist, dental laboratory, and other dental professionals engaged in the treatment process to communicate and collaborate effectively. The digital records, including the virtual mock-up, serve as a visual reference for communicating the desired objectives and providing exact directions for producing restorations or aligning treatment goals.
Functional and aesthetic elements are taken into account when designing the treatment. The dentist ensures that the procedures offered not only improve the aesthetics of the smile, but address any underlying dental disorders, restore appropriate occlusion, and improve oral function. It is an all-encompassing strategy that aims for both a beautiful smile and long-term dental health.
The treatment plan is thoroughly reviewed with the patient. The dentist discusses the planned procedures, advantages, and potential dangers or limits. The patient has the opportunity to ask questions, provide feedback, and provide informed consent for the planned therapies.
The Digital Smile Design Treatment Planning stage is critical for generating a complete and tailored treatment plan. The dentist ensures that the suggested procedures correspond with the desired smile design, functional needs, and the patient's expectations by leveraging digital records and virtual mock-ups.
8. Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration take place between the dentist, dental laboratory, and other dental professionals engaged in the treatment process during the Communication and Collaboration step of Digital Smile Design. The stage ensures that all parties are on the same page with the treatment objectives and that they are working together to accomplish the desired smile makeover.
The digital data are shared with the dental laboratory and other relevant experts by the dentist, which include intraoral scans, extra-oral pictures, radiographic images, and a virtual mock-up. These digital records serve as a visual reference and accurate information for constructing restorations and coordinating treatment goals.
The dentist and dental laboratory personnel hold collaborative discussions to discuss the treatment plan and the specific requirements for producing restorations. It allows for open discussion, the resolution of any doubts or issues, and the assurance that all parties understand the desired goals.
The dentist works with the dental laboratory to integrate the digital smile design into the computer-aided design (CAD) program when using computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology. The collaboration guarantees that the virtual design is converted precisely into actual restorations.
The dental laboratory fabricates the necessary restorations, such as veneers, crowns, or bridges, based on the virtual mock-up and treatment plan. The digital records and detailed instructions offered during the communication and collaboration process aid in ensuring that the restorations fit the required criteria.
The dentist works with orthodontists, prosthodontists, and other experts to make accusal changes or other functional issues. They collaborate to ensure that the proposed grin design not only meets cosmetic objectives but restores adequate occlusion and functional harmony.
The dentist often communicates with the dental laboratory and other experts involved throughout the treatment procedure. It enables progress updates, feedback exchange, and addressing any necessary revisions or refinements.
The dentist coordinates the sequencing and scheduling of treatment operations, ensuring that all experts involved are aware of the plan and their respective tasks. The collaboration aids in the treatment process by providing a consistent approach to reaching the targeted smiling outcomes.
Effective communication with the patient is maintained throughout the treatment procedure. The dentist keeps the patient informed of developments, resolves any concerns, and provides any instructions or direction that is required. The partnership means that the patient is kept informed and actively involved in the process of transforming their smile.
Digital Smile Design promotes a collaborative approach among dental professionals participating in the treatment process by stressing communication and collaboration. It allows for fast data sharing, collaborative consultations, and regular updates, ensuring that everyone is on the same page in terms of obtaining the intended smile outcomes while retaining patient satisfaction.
9. Implementation
The planned treatment plan is put into action during the Digital Smile Design Implementation process to accomplish the desired smile makeover. The step entails carrying out the planned operations, making use of digital records, and working together.
The dentist starts by preparing the patient for the procedures described in the treatment plan. Local anaesthetic, sedation, or other preparations used to ensure the patient's comfort throughout treatment.
The dental laboratory fabricates them based on the virtual mock-up and specific instructions if restorations like veneers, crowns, or bridges are part of the treatment plan. The restorations are subsequently placed on the patient's teeth by the dentist, assuring a perfect fit, aesthetics, and functional alignment.
The dentist or orthodontist implements the essential measures to align the teeth and obtain the desired smile outcomes in the case of orthodontic procedures such as braces or aligners. It entails periodic changes and progress assessments.
The dentist performs the necessary operations to obtain the ideal gingival aesthetics and symmetry if gum contouring or reshaping is required. It includes laser treatments, gingivectomy, or gum grafting.
The dentist performs it to reach the desired tooth colour if teeth whitening or bleaching is part of the treatment plan. It includes giving in-office professional whitening treatments or take-home whitening kits with custom-fitted trays.
The dentist checks to make sure the occlusion or bite is properly aligned and functional. Any changes that are required to ensure that the teeth fit together nicely and provide excellent chewing performance are made.
The dentist reviews the results to confirm that the anticipated smile outcomes have been obtained following the completion of the planned procedures. It includes evaluating the patient's looks, function, and overall satisfaction.
The dentist maintains communication and collaboration with the dental laboratory, orthodontists, and other treatment professionals throughout the Implementation phase. It ensures that the execution is consistent with the treatment plan and that any tweaks or alterations are made as needed.
The active execution of the treatment plan using digital records, restorations, orthodontic treatments, gum contouring, and other procedures is the Implementation stage. The dentist works towards attaining the intended smile transformation and delivering a beautiful, functional, and harmonious smile for the patient by following the scheduled phases and leveraging the digital smile design.
10. Evaluation and Maintenance
The dentist focuses on reviewing the outcomes of the implemented treatment plan and assuring the long-term success and maintenance of the patient's new smile during the Evaluation and Maintenance step of Digital Smile Design. Several essential actions are required to monitor the outcomes, resolve any concerns, and provide recommendations for continued treatment.
The dentist performs a post-treatment evaluation to examine the outcomes of the treatment plan. The comprehensive examination includes examining the patient's aesthetics, function, and satisfaction. The dentist confirms that the desired smile transformation has been achieved by comparing the achieved results to the initial smile design and treatment goals.
The dentist makes the appropriate changes to further improve the aesthetics or function of the smile if any minor tweaks or fine-tuning are required. It entails fine-tuning the bite alignment, resolving any minor inconsistencies, or making modest adjustments to the restorations or orthodontic appliances.
The dentist advises the patient on proper dental hygiene and care routines to ensure the health and longevity of the new smile. It includes teaching the patient effective brushing and flossing procedures, recommending appropriate oral care products, and emphasising the significance of frequent dental check-ups and cleanings.
Follow-up sessions are planned to assess the long-term stability and success of the smile change. The dentist checks the dental health, assesses the endurance of the restorations, and handles any concerns or issues that develop during these appointments.
The dentist recommends the use of retainers, sleep guards, or other equipment to ensure the alignment and stability of the teeth and restorations. The need for constant use and good maintenance of these appliances is explained to the patient.
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are recommended to monitor oral health, uncover any concerns, and ensure the smile transformation's lifetime. The dentist performs routine examinations, collects appropriate radiographs, and provides essential preventive treatment.
The Evaluation and Maintenance stage includes ongoing patient education and support. The dentist is always accessible to discuss any issues or questions that the patient has, as well as to provide ongoing advice on oral health, smile maintenance, and any prescribed treatments. The dentist provides resources or recommendations to ensure that the patient receives thorough care if the patient requires specialised care.
The dentist assures the long-term success and pleasure of the digital smile design during the Evaluation and Maintenance process. The dentist assists the patient in maintaining a beautiful, functional, and healthy smile for years to come by routinely examining the results, making necessary modifications, and offering instructions for continued maintenance.
How long is the procedure for Digital Smile?
The initial consultation typically lasts 30 minutes to an hour, while the comprehensive evaluation takes up to 2 hours, involving multiple sessions and diagnostic procedures. The duration of the Digital Smile Design (DSD) process varies depending on the specific procedures and treatments involved.
Digital imaging, smile analysis, tooth design, and virtual mock-up creation each require varying amounts of time, ranging from 30 minutes to several hours. Treatment planning duration depends on the complexity of the case.
Implementation spans from a few hours to multiple appointments over weeks or months. The evaluation and maintenance phase, including post-treatment evaluations and follow-up sessions, are ongoing and crucial for long-term success. These time estimates are approximate and subject to variation based on individual treatment plans and patient needs.
How long is the recovery for Digital Smile?
Full healing takes one to two weeks. The recovery period for Digital Smile Design varies depending on the precise treatments used and the healing process of the individual patient. Digital Smile Design involves a wide spectrum of dental procedures, and recuperation times vary.
Some patients suffer slight sensitivity or discomfort for a few days following the insertion of restorations like veneers or crowns. The gums and surrounding tissues require time to adjust to the new restorations.
The recovery period for orthodontic treatments such as braces or aligners varies based on the complexity of the case and the individual's response to the therapy. Some discomfort or soreness is normal in the days following adjustments or changing aligners. The recuperation time for orthodontics range from several months to a few years, depending on the treatment strategy.
Gum contouring or reshaping techniques cause moderate discomfort and swelling soon following the procedure. These symptoms, however, normally go away within a few days to a week. Full recuperation and completion of the project take numerous weeks.
Teeth whitening treatments, particularly in-office professional whitening, require little to no recovery time. Some people have temporary tooth sensitivity, which usually disappears after a few days. The period of recovery for take-home whitening kits is determined by the frequency and duration of use, as prescribed by the dentist. The majority of patients attain their desired whitening outcomes in a few weeks.
Is It Possible to Design Aesthetic Teeth with Digital Smile Design?
Yes, it is possible to design aesthetic teeth with digital smile design. Digital Smile Design (DSD) is created to assist dentists and patients in creating aesthetically pleasing and harmonious smiles. Digital Smile Design enables dentists to assess the patient's facial features, tooth structure, and smile proportions in great detail by utilising advanced digital technology and imaging software. It allows detailed planning and customisation of the smile design to reach the desired aesthetic results.
Dentists use DSD to examine tooth shape, size, position, alignment, and colour to develop a personalised smile design that enhances the patient's facial appearance. DSD's digital tools and virtual mock-ups enable precise alterations and fine-tuning of the smile design to achieve the best aesthetic outcomes.
Dentists efficiently communicate and collaborate with dental laboratories and other specialists to create restorations that fit with the desired aesthetic goals by harnessing the capabilities of digital technology. The use of digital records and virtual simulations allows for the accurate manufacturing and placement of veneers, crowns, and other dental restorations to obtain the desired aesthetic result.
How much is a Digital Smile procedure in Turkey?
The cost of a Digital Smile operation ranges from around £1,500 to £10,000 or more in Turkey. Comprehensive examinations, digital imaging, smile analysis, virtual mock-ups, treatment planning, restorations, like veneers, crowns, orthodontic treatments, gum contouring, tooth whitening, follow-up consultations, and maintenance are all included in therange.
The cost of a Digital Smile design in Turkey process varies depending on several factors, including the specific treatments required, the complexity of the case, the location of the dental office, and the dentist's skill.
The cost varies greatly depending on individual circumstances and the exact treatment plan tailored to the needs. It is recommended to arrange a consultation with a dentist or dental professional who offers a personalised estimate based on specific needs.
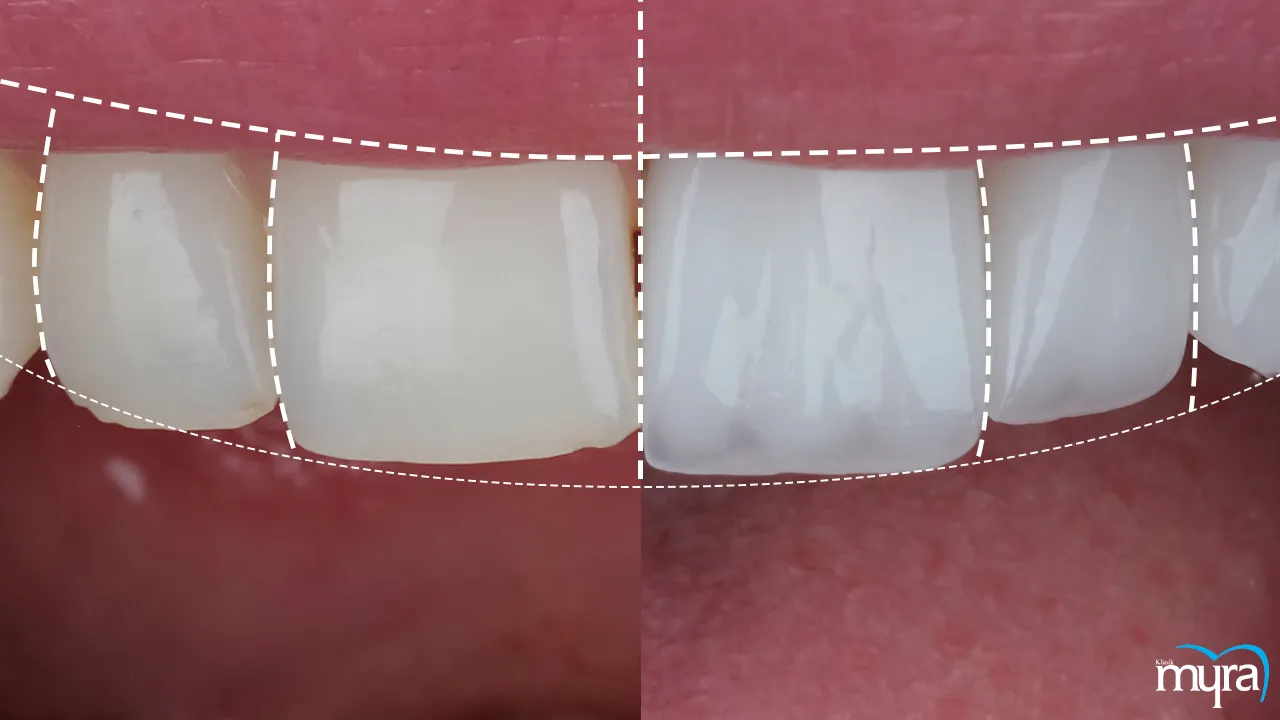
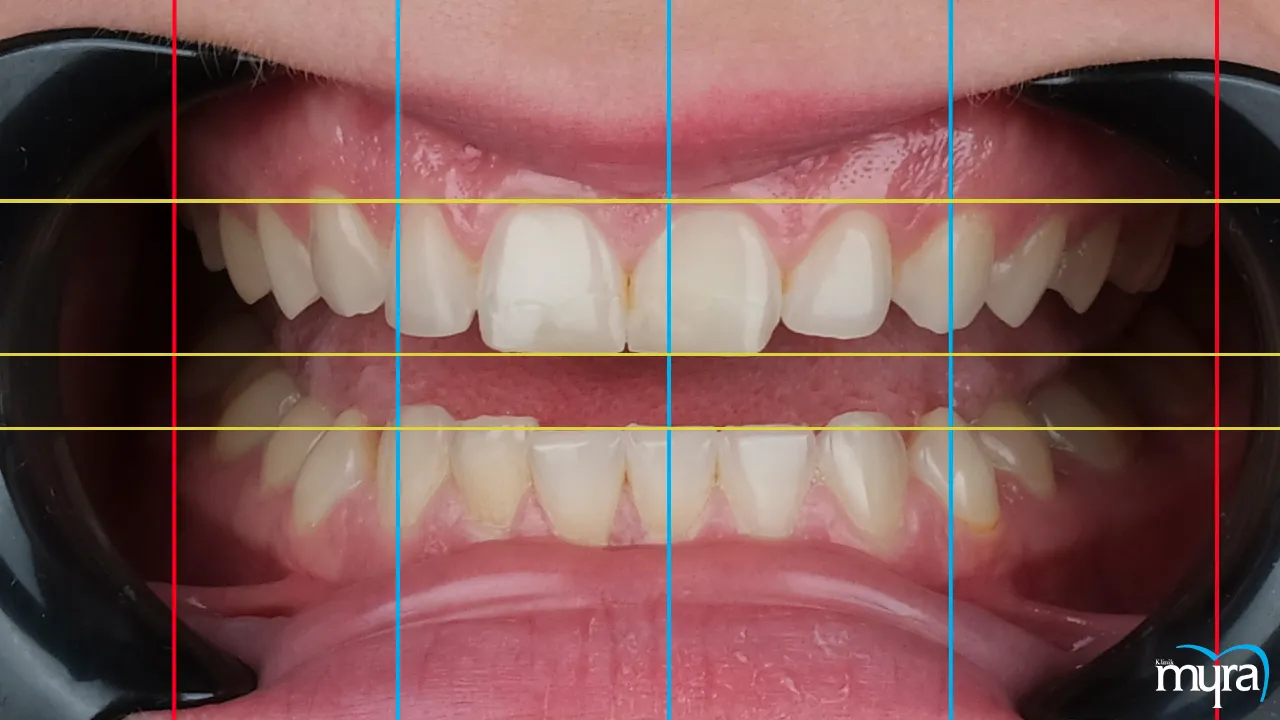
What are the different principles of Smile Design?
There are top five principles of smile design. These five main principles are facial harmony, smile line and midline alignment, tooth proportions and golden proportions, tooth shape and contour, and colour and shade.
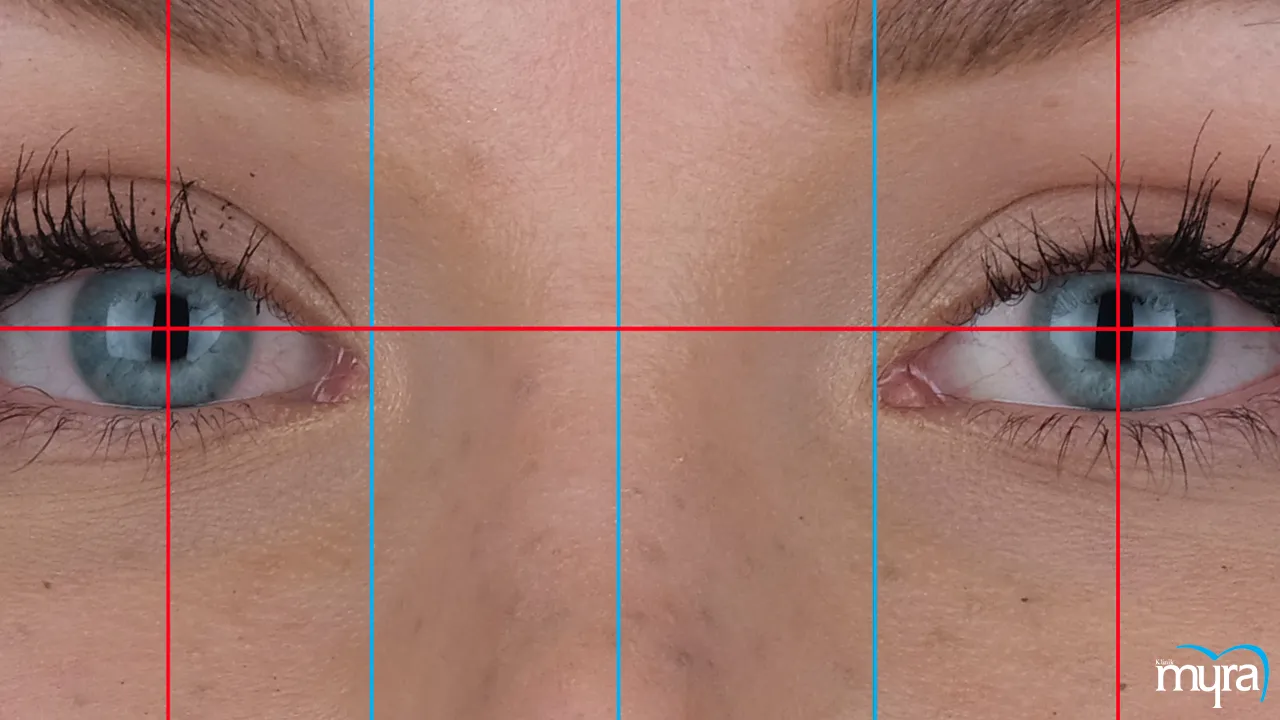
Facial harmony is a fundamental principle that considers factors such as the shape of the face, symmetry, lip position, and facial aesthetics. A natural and balanced appearance is achieved by designing a smile that complements the individual's unique facial characteristics.
Smile line and midline alignment is another principle. The smile line must follow the contour of the lower lip for an aesthetically pleasing result formed by the edges of the upper teeth when smiling. Ensuring that the centre line of the upper front teeth aligns with the centre of the face contributes to a harmonious and symmetrical smile.
Tooth proportions and the concept of the Golden Proportion play a crucial role in Smile Design. The Golden Proportion is a mathematical ratio found in nature and art that helps achieve harmonious tooth proportions. It involves considering the width-to-length ratio of the front teeth and their relationship to adjacent teeth, resulting in a pleasing smile.
The shape and contour of individual teeth are one of the essential principles of Smile Design. Teeth must have a natural and pleasing shape that complements the patient's facial features and gender. Considerations such as tooth size, incisal edge position, and tooth contour contribute to the aesthetics of the smile.
The colour and shade of the teeth are vital aspects of Smile Design. Achieving an appropriate tooth shade that suits the patient's complexion, age, and personal preferences is essential for a natural and attractive smile. Factors such as tooth colour harmonisation, brightness, and translucency are considered to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome.
What are the advantages of Digital Smile Design?
Listed below are the advantages of Digital Smile Design.
- Improved Communication: DSD allows for better communication between the dentist and the patient. The dentist visually exhibits and explains the recommended smile design to the patient using digital technology. The graphic representation helps the patient grasp the predicted outcomes, allowing for effective communication and joint decision-making.
- Anticipated Results: DSD enables exact planning and visualisation of the result before any therapy. The dentist precisely plans and forecasts the predicted outcomes of various treatment options by using digital imaging, virtual mock-ups, and smile simulations. It improves therapy predictability and helps patients set realistic expectations.
- Modified Treatment: The dentist tailors the treatment plan to the patient's individual needs and desires with DSD. The dentist modified the smile design to get a personalised and natural-looking result by analysing the patient's facial features, tooth structure, and smile proportions. The personalisation guarantees that the patient's distinct features are considered, resulting in a more satisfying conclusion.
- Increased Patient Satisfaction: The collaborative nature of DSD, with the patient actively engaging in the smile design process, increases patient satisfaction. The patient's choices and feedback are taken into account, boosting their engagement and involvement in the process throughout the treatment planning stage. Participation develops a sense of ownership and satisfaction with the finished product.
- Efficiency in Time and Cost: DSD expedites the treatment process and optimises resource use, saving time and money. The dentist correctly arranges the treatment using digital technology, avoiding the need for many changes or revisions. It saves the dentist and the patient time. DSD enables better utilisation of materials and resources, potentially leading to cost savings.
- Better Collaboration: DSD encourages smooth communication between the dentist and other specialists involved in the treatment process. Digital records and virtual simulations are easily shared and discussed with dental laboratories, orthodontists, and other experts, ensuring a coordinated and efficient treatment strategy.
- Continuing Education and Development: DSD offers chances for dentists to improve their aesthetic dentistry skills and knowledge. Dentists broaden their expertise, improve patient care, and contribute to their professional development by embracing digital technology and staying up to date on the newest innovations in DSD.
What are the disadvantages of Digital Smile Design?
Listed below are the disadvantages of Digital Smile Design.
- Expensive equipment, software, and training: Investing in digital equipment, software, and training to implement DSD raises the cost of dental practices. It results in higher expenditures for patients seeking DSD operations when compared to typical treatment choices.
- Additional Training: Dentists and dental workers need additional training and time to become proficient in using DSD-related digital tools and software. The learning curve initially stymies the integration of DSD into the practice and necessitates continual education to keep up with the most recent improvements.
- Dependence on Technology: Run the danger of technical faults, software compatibility concerns, or equipment failures when relying on digital technology. Any interruptions in the digital workflow impair treatment planning temporarily or cause delays in delivering the intended results.
- Absence of Tactile Feedback: Tactile feedback is used by dentists in traditional smile design procedures to analyse the texture, fit, and occlusion of restorations. The use of digital images and virtual simulations with DSD limits the ability to physically assess certain elements. It requires extra tweaks or fine-tuning during the implementation phase.
- Limited in some areas: DSDs are not generally available in all dental practices, particularly in isolated places or regions with limited access to advanced digital technologies. It limits patients' access to DSD operations, requiring them to travel or seek out specialised doctors.
Is Digital Smile Design better than the traditional smile design?
Yes, the digital smile design is better than the traditional smile design because a digital smile is more detailed and accurate than the traditional smile design. DSD allows dentists to create a “preview” of the final smile before any procedure is done. The patient sees what their new smile looks like and makes sure they are happy with the results before any work is done.
Digital Smile Design (DSD) and traditional smile design have pros and cons. One method is better than the other and relies on many things, such as the specific case, the dentist's skills, and what the patient wants. Each method has its pros and cons, and which one chooses must depend on a specific situation.
Can Digital Smile Design evaluate and enhance a gummy smile?
Yes, digital smile design evaluates and enhances a gummy smile. Dentists look at how the gum line and teeth look about the whole smile by using computer imaging and software. The dentists make a custom smile design that takes into account the problems that come with a gummy smile.
The dentist models the changes the patient wants and works with the patient to improve the design by changing the images digitally. Use treatments like gum contouring, crown lengthening, or braces to get the desired result. DSD gives a complete set of tools to evaluate and improve a gummy smile, giving the patient a more balanced and physically pleasing smile.
What is the difference between Digital Smile Design and Smile Design?
Listed below are the differences between digital smile design and smile design.
- Digital Smile Design is a modern approach that utilises digital technology, including imaging software and virtual simulations, to analyse and design smiles. Smile Design is a broader term for the process of designing smiles using standard methods and tools, such as manual evaluations, physical mock-ups, and artistic principles.
- Digital Smile Design excels at showing how the planned smile design looks and making it easier for the dentist and the patient to talk to each other. Smile Design depends more on verbal explanations, physical models, and artistic interpretations, which are not the best way to show exactly how something looks.
- Digital imagery, intraoral scanning, and computer software power DSD. Digital tools improve smile design accuracy, efficiency, and communication. Smile Design uses manual diagnostic tools that are less precise and efficient.
- Dentists must master digital tools and software for DSD. Implementing DSD in dental practices requires some training. Smile Design techniques are easier to learn and practise.





