A tooth abscess is a bacterial infection that causes pus buildup in the gums or teeth, causing severe pain, swelling, fever, and pus drainage. Understanding tooth abscess symptoms, treatment, and causes helps with early detection, complication avoidance, timely treatment, oral health promotion, pain management, anxiety reduction, and financial implications. It helps manage pain, make informed decisions, and reduce fear of dental procedures.
Tooth abscess symptoms include fever, bad breath, sensitivity to temperature changes, pain when chewing, and facial, cheek, or neck swelling. The other symptoms include severe, constant, throbbing toothaches and tender, swollen lymph nodes under the jaw or neck. The symptoms indicate the body's active fight against the infection, causing inflammation and pus accumulation. The body's immune response to the infection affects the lymphatic system, activating the lymph nodes to fight off bacteria.
Tooth abscess treatments include incision and drainage, tooth extraction, root canals, antibiotics, and removing foreign objects. Incision and drainage involve a dentist making a small incision to drain pus and prevent infection. Tooth extraction removes the infection source and promotes healing. Root canals remove and preserve the tooth's pulp chamber and canals. Antibiotics are prescribed to target and eliminate bacteria from infection. Removal of foreign objects involves identifying and extracting the source of infection.
Severe cavities, dental caries, tooth decay, broken teeth, gum disease, injury to the tooth, poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, smoking, and a weakened immune system cause tooth abscesses. Cavities form when bacteria erode the enamel, while broken teeth compromise the tooth structure, allowing bacteria to enter the pulp. Gum disease causes gums to pull away from teeth, creating pockets filled with bacteria and plaque. Injuries to the tooth, poor oral hygiene, dry mouth, smoking, and a weakened immune system contribute to tooth abscesses.
Tooth decay and tooth abscesses are related but have distinct causes. Tooth decay is a gradual breakdown of a tooth's structure, while tooth abscess is an infection causing pus pockets. Poor oral hygiene and plaque buildup are the leading causes of tooth decay and cavities. Treatments vary depending on the severity of the condition, with restorative dental procedures used for early and advanced decay requiring crowns. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups helps manage dental conditions.
A study by Jose F. Siqueira and Isabela N. Rocas explores the link between oral bacteria and brain abscesses, a type of dental abscess caused by root canal infection. The study examines the aetiology, causes, and treatment of acute apical abscesses, a dental abscess resulting from a tooth's root canal infection. Dr Raul Bescos and Dr Zoe Brookes' research found that bacteria causing oral infections contribute to life-threatening brain abscesses in patients. The study, published in the Journal of Dentistry, found that patients with no apparent cause of brain abscesses had higher counts of Streptococcus anginosus, a bacteria that causes pharyngitis, bacteremia, and infections in internal organs.
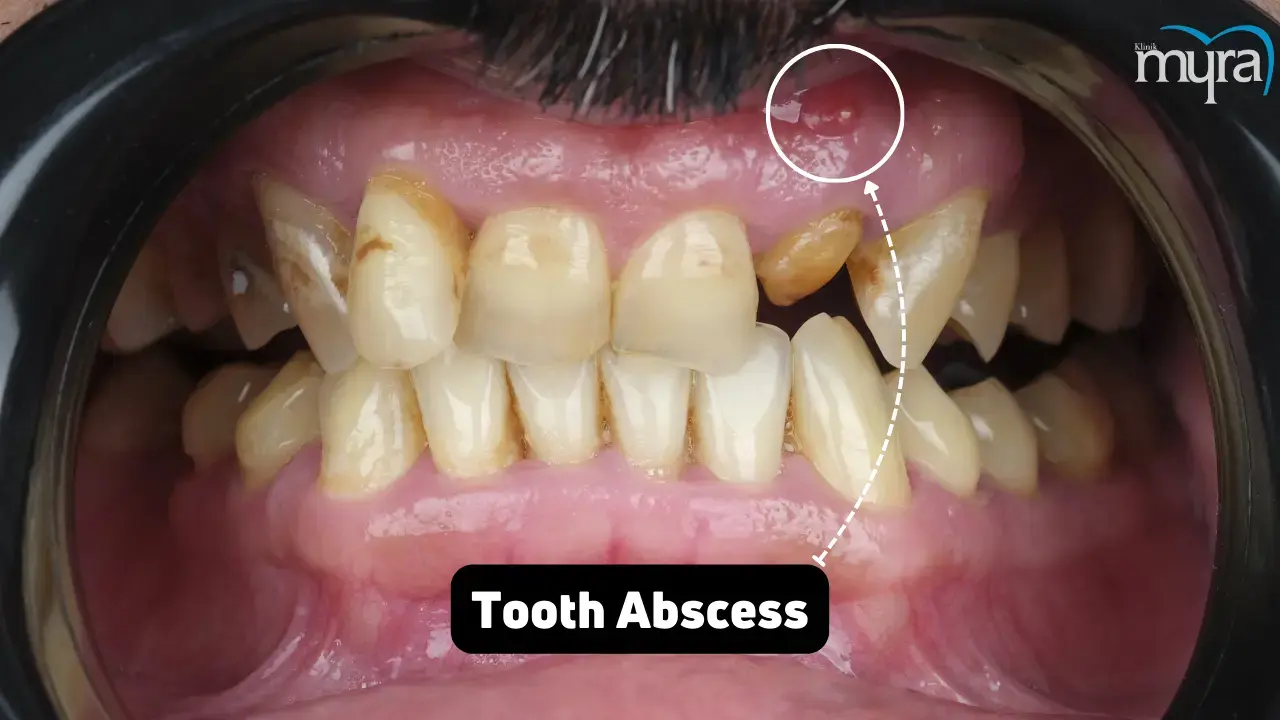
What is Tooth Abscess?
A tooth abscess is a bacterially induced pocket of pus that results from gum disease, trauma, or serious tooth decay. It occurs at the root tip or gums on the side of a tooth root. A tooth abscess affects the gums on the side of a tooth root or the tip. The infection harms the tissues in the mouth and has the opportunity to spread to other body parts, leading to widespread health problems.
A dentist must treat an infected tooth because it won't cure itself. A dental abscess is a buildup of pus inside the gums or teeth that frequently results from bacterial infections that have spread throughout the tooth's delicate pulp. Tooth abscesses cause severe toothache, swelling, fever, and sometimes pus drainage. Treatment involves draining the abscess and includes a root canal or tooth extraction to eliminate the infection. A dental abscess is considered a type of gum problem, it originates from or affects the gum tissues surrounding the teeth.
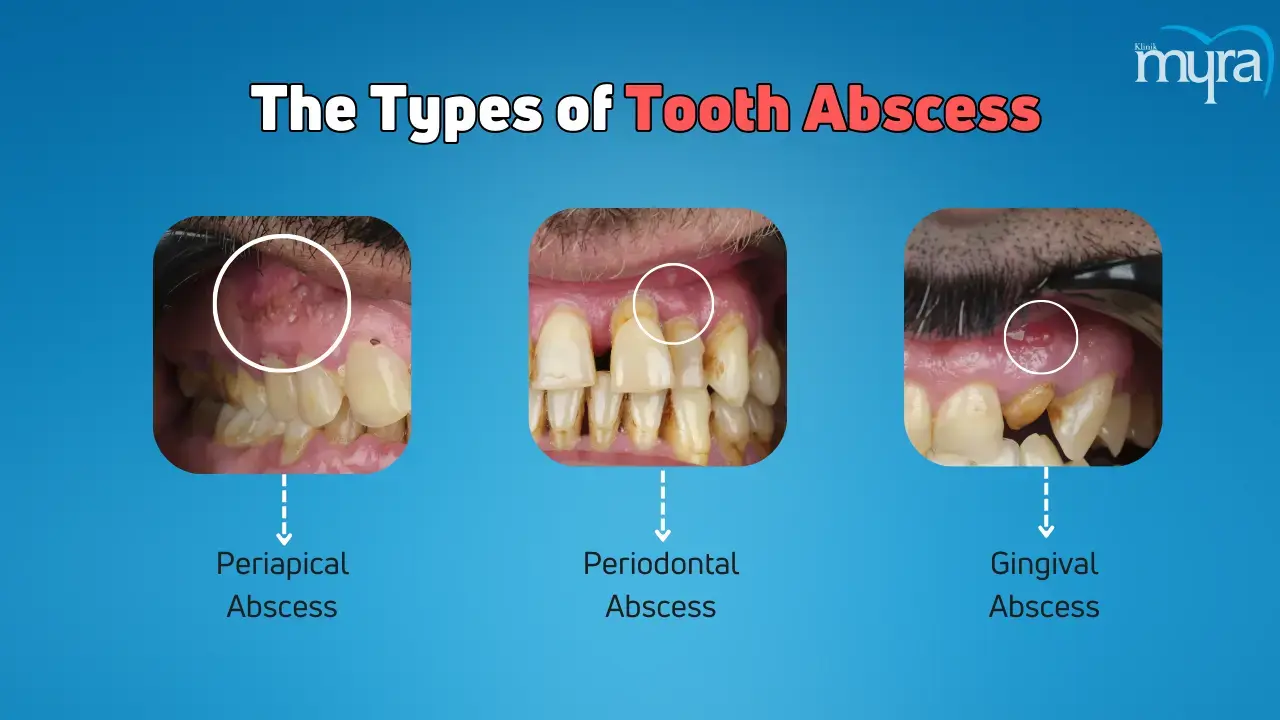
What are the Types of Tooth Abscess?
The types of tooth abscess are listed below.
- Periapical Abscess: Periapical abscess is a dental emergency resulting from a dental damage or cavity. It concerns the top of the tooth and results from a bacterial infection of the pulp, the tooth's innermost layer. The disease spreads to nearby teeth or roots, causing systemic symptoms such as fever or malaise. Treatment involves a root canal or tooth extraction to remove the infection, which leads to severe toothache, swelling, and pus formation.
- Periodontal Abscess: A periodontal abscess is a gum infection near a tooth's root resulting from periodontitis, a severe gum disease that causes tooth loss. It presents with swollen red gums and does not cause large cavities in surrounding teeth. Periodontal abscesses share a microbiology similar to periodontal disease, involving inflammation and infection of the gums and bone-supporting teeth. The bacteria involved are resistant to antibiotics, except for azithromycin.
- Gingival Abscess: A gingival or gum abscess is a painful infection of the gums that spreads to other parts of the mouth. It causes pain, swelling, and redness at the gum line and results from external damage or gum disease. Early treatment is needed to prevent further complications.
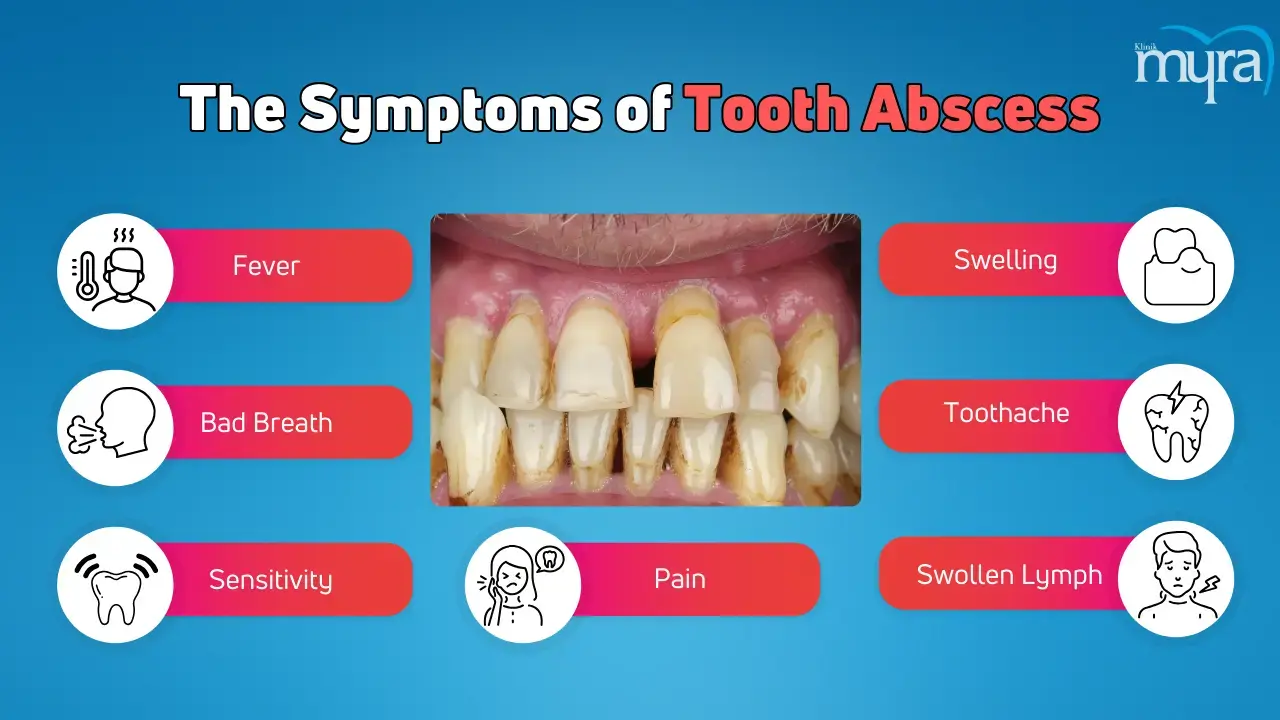
What are Tooth Abscess Symptoms?
The tooth abscess symptoms are listed below.
- Fever: Fever is a symptom that suggests the infection is spreading beyond the localised area. The immune system releases pyrogens, which travel to the hypothalamus in the brain, regulating body temperature. The systemic response indicates the body is actively fighting the infection. A severe infection includes a fever, facial or neck swelling, and difficulty breathing or swallowing.
- Bad Breath: Bad breath, or halitosis, is a symptom of a tooth abscess caused by a bacterial infection. The bacteria produce sulphur compounds and other foul-smelling substances, released as bacteria break down tissue and multiply within the abscess. Pus drains from the abscess into the mouth, leading to a sour taste and odour. Necrotic tissue in and around the abscess dies, contributing to the foul smell. Reduced oral hygiene due to pain and swelling makes it difficult for patients to maintain proper oral hygiene, allowing food particles and bacteria to accumulate, further contributing to bad breath.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold: The infection and inflammation cause nerves in the dental pulp to become more sensitive to temperature changes, leading to sharp, shooting pain or a dull ache. The sensitivity has the potential to be continuous or occur at times when consuming hot or cold substances. The pain response to hot or cold substances is intense and lingers even after removing the stimulus, distinguishing it from typical tooth sensitivity.
- Pain when Chewing: Tooth abscesses cause pain when chewing, characterised by throbbing, gnawing, or sharpshooting. The discomfort radiates to the jaw, ear, and neck due to the pressure exerted on the infected tooth, which irritates nerves and surrounding tissues. The pressure on the infected area compresses the inflamed tissues and the pus-filled pocket, causing pain.
- Swelling in the face, cheek, or neck: Tooth abscesses cause severe swelling in the face, cheek, or neck due to the spread of infection from the tooth to surrounding tissues. The swelling leads to difficulty breathing or swallowing. The body's immune response to the tooth infection results in visible swelling due to the body's fight against the infection.
- Severe, constant, throbbing toothache: A severe, constant, throbbing toothache is a common symptom of a tooth abscess caused by infection and inflammation affecting the tooth's nerve. The pain spreads to the jawbone, neck, or ear and worsens over time. It is a sign that immediate dental care is needed to treat the underlying infection. A dental abscess results from bacterial infection due to untreated tooth decay, gum disease, or trauma. The infection causes the death of dental pulp tissue, leading to pus formation. The body's immune response causes inflammation and pus accumulation, creating pressure within the tooth and surrounding tissues and causing severe pain.
- Tender, swollen lymph nodes under the jaw or neck: Tender, swollen lymph nodes under the jaw or neck indicate a tooth abscess, as part of the body's immune system, and become swollen when responding to an infection. A dental abscess starts as a localised infection in the tooth or gums that spreads to surrounding tissues, including the lymph nodes. The lymphatic system, which plays a role in the body's immune response, activates the lymph nodes to fight off bacteria.
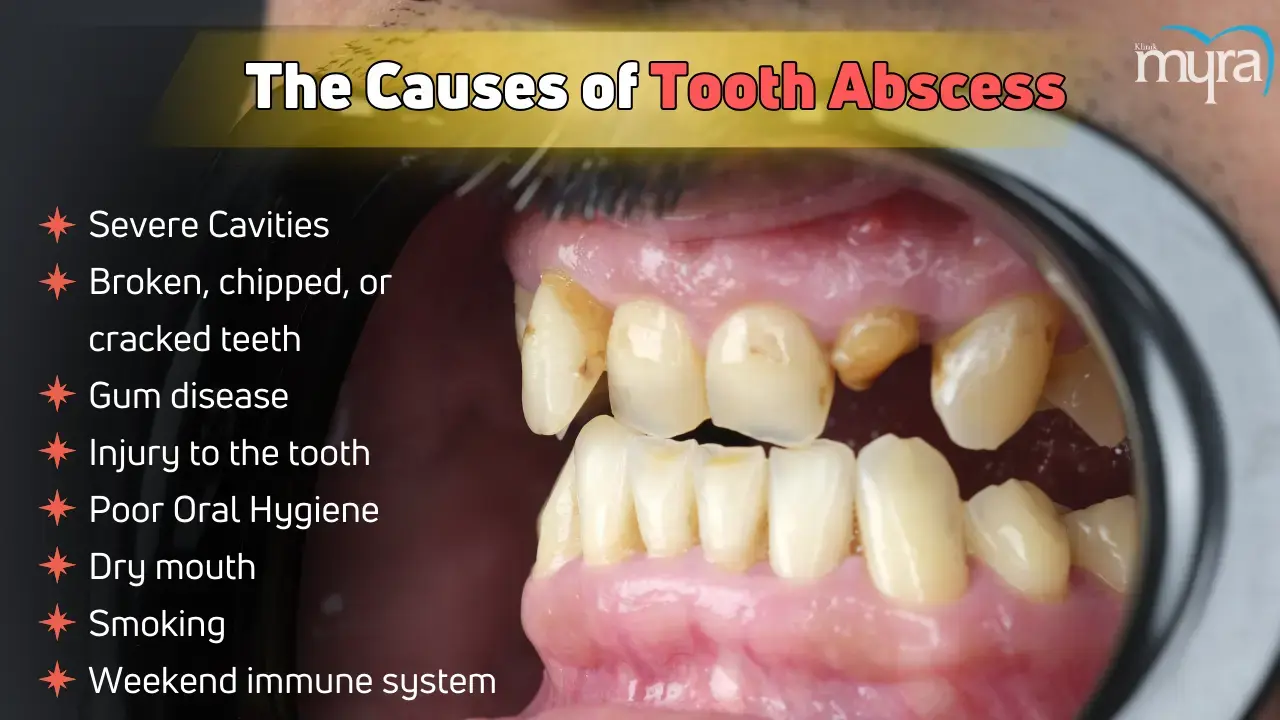
What are the Causes Tooth Abscess?
The causes of tooth abscess are listed below.
- Severe Cavities: Severe cavities, dental caries, or tooth decay lead to tooth abscesses by allowing bacteria to penetrate deep into the tooth. Cavities form when bacteria erode the enamel. Poor oral hygiene, sugary foods, and inadequate fluoride exposure contribute to the development of cavities. The tooth becomes more sensitive to stimuli as the cavity deepens and enters the dentin. Inflammation and infection are the consequences of caries that spread to the dental pulp if left untreated.
- Broken, chipped, or cracked teeth: Tooth abscesses occur when bacteria enter a tooth through cracks, chips, or breaks, infecting the pulp inside. It causes swelling and inflammation at the root tip and spreads to the jawbone or facial tissues if left untreated. Broken, chipped, or cracked teeth compromise the tooth structure, exposing the inner layers and allowing bacteria to penetrate deeper. Bacteria invade the dentin, reaching the dental pulp and causing inflammation and infection. If untreated, the pulp tissue dies, leading to an abscess, a pocket of pus.
- Gum disease: Gum disease, or periodontitis, causes gums to pull away from teeth, creating pockets filled with bacteria and plaque. The infection leads to tooth abscesses, which are the cause. Gum disease begins with gingivitis, an inflammation caused by plaque accumulation. Deep pockets between teeth and gums become filled with bacteria, plaque, and tartar, which can cause bacterial infection, leading to loose teeth and periodontal abscesses.
- Injury to the tooth: Tooth injuries cause dental abscesses by damaging the tooth's structure, allowing bacteria to infiltrate and cause infection. Injuries include physical trauma, cracks or fractures, or knocked-out teeth. The compromised tooth structure exposes the enamel, dentin, or pulp, allowing bacteria to invade. Severe damage reaches the dental pulp, leading to inflammation and infection. Abscesses develop at the tooth root tip or in surrounding gum tissue.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Poor oral hygiene is a cause of tooth abscesses due to the formation of dental plaque, tooth decay, gum disease, and bacterial invasion. Dental plaque, a sticky, colourless film of bacteria, hardens into tartar when not removed through brushing and flossing. Bacterial infections cause the body to mount an immune response, leading to pus accumulation and abscesses. Regular dental care helps with prevention.
- Dry mouth: Dry mouth, or xerostomia, increases the risk of tooth decay and abscess tooth due to reduced saliva production, bacterial growth, and cavities. Saliva helps cleanse teeth and neutralise bacteria's acids, but the mouth becomes acidic without it, leading to decay. Bacteria feed on food particles, producing acids that erode tooth enamel and cause tooth decay. Cavities progress deeper into the tooth structure, reaching the dental pulp. Bacterial invasion and infection lead to inflammation and plaque formation.
- Smoking: Smoking leads to tooth abscesses by weakening the immune system, preventing the healing of the abscess, and reducing saliva production. Smoking increases the risk of gum disease, delaying healing, altering the oral microbiome, and compromising blood circulation. Nicotine and tar prevent the abscess from healing, leading to a dry mouth. Smoking weakens the body's ability to fight infections, making the gums and oral tissues vulnerable. Compromised blood circulation slows the healing process, making the tooth susceptible to damage and infection. Smoking alters the balance of bacteria in the mouth, promoting the growth of harmful bacteria that contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Weekend immune system: A weakened immune system leads to tooth abscesses by reducing the body's ability to fight off bacterial infections in the mouth. It increases susceptibility to infections, compromised bacterial control, and delayed healing. Chronic health conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, cancer, and autoimmune disorders weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of dental infections and abscesses. A compromised immune system exacerbates oral health issues, creating pockets between teeth and gums for bacteria to thrive, leading to gum abscesses. Patients with a weakened immune system must take extra precautions to mitigate the risk of developing severe and painful dental conditions.
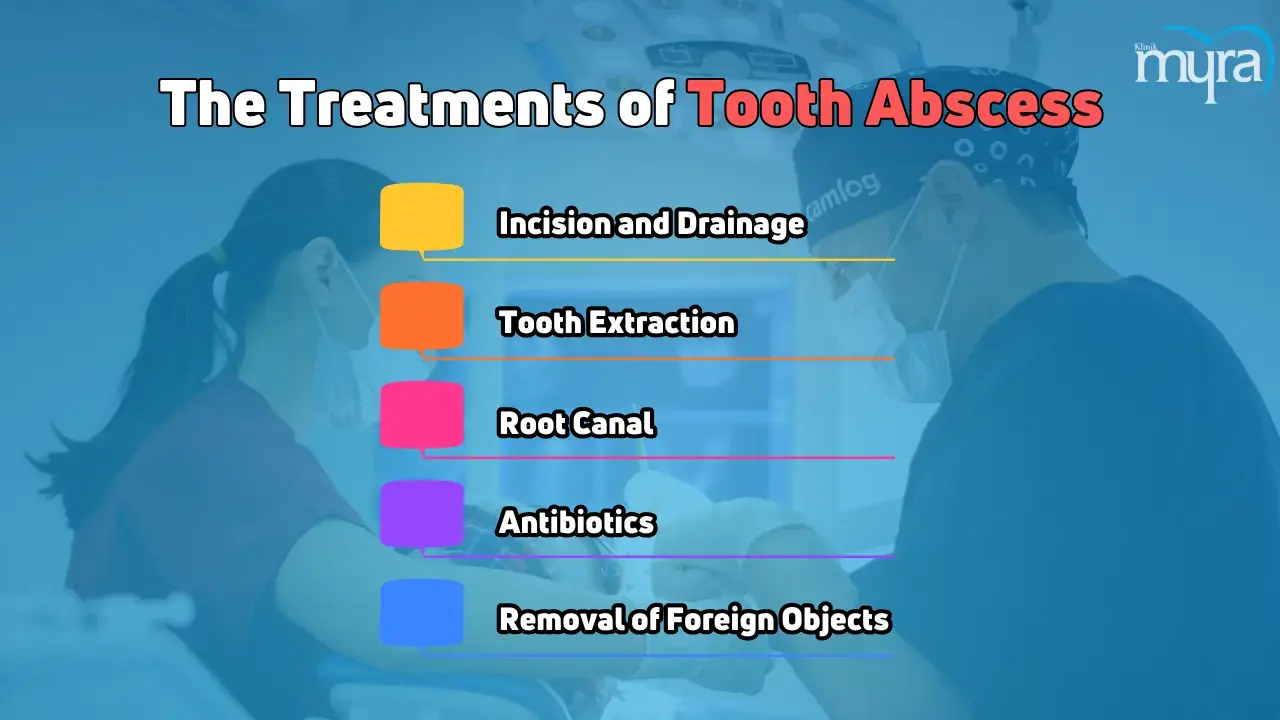
What are the Tooth Abscess Treatment?
The tooth abscess treatments are listed below.
- Incision and drainage: Incision and drainage is a treatment for tooth abscesses, a localised collection of pus caused by bacterial infection. It involves a dentist making a small incision to drain the pus and placing a rubber drain to keep the area open. The procedure reduces swelling and discomfort and prevents the spread of infection. The dentist numbs the area with local anaesthesia and then makes a small cut into the abscess to allow the pus to escape. The area is then cleaned and disinfected to promote healing. Patients are prescribed antibiotics and pain relievers to manage discomfort during the recovery period.
- Tooth Extraction: Tooth extraction is a treatment for severe tooth abscesses where root canal therapy is ineffective. It involves a dentist administering local anaesthesia, loosening tissue, and gently removing the tooth from its socket. The area is cleaned to prevent further infection, and a dental bone graft is placed to reduce the risk of bone loss. The goal is to remove the infection source and promote healing. Post-operative care includes gauze pad biting, pain management medications, and antibiotics. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are emphasised to maintain oral health and prevent future abscesses or complications.
- Root Canal: A root canal is a surgical procedure that removes and preserves a tooth abscess by eliminating the infection and keeping the tooth's pulp chamber and root canals. The dentist drills into the tooth to remove the diseased tissue and drain the abscess, then cleans, shapes, and fills the canals with a sealing material to prevent further root infection. The treatment eliminates bacteria from the infected root canal, prevents reinfection, and saves the natural tooth. Patients experience mild discomfort or sensitivity post-procedure but manage pain with over-the-counter pain medications or antibiotics if the infection is severe.
- Antibiotics: Dentists prescribe antibiotics to treat tooth abscesses by targeting and eliminating the bacteria causing the infection. Antibiotics help reduce the spread of disease, alleviate pain and swelling, and prevent further complications. Prescribed antibiotics include amoxicillin, clindamycin, and metronidazole. Antibiotics kill the bacteria outright or stop the bacteria's growth and reproduction. Patients should take antibiotics as prescribed and complete the course, even if symptoms improve or disappear before the medication is finished.
- Removal of foreign objects: The removal of foreign objects is a treatment for tooth abscesses, involving the dentist identifying and extracting any foreign material that caused the infection. It includes food particles, broken teeth, or debris lodged in the gums or teeth. The area is thoroughly cleaned with a saline solution to eliminate the source of infection and allow the abscess to heal appropriately. Post-procedural care instructions include pain management, oral hygiene practices, and follow-up appointments to monitor healing. The treatment alleviates pain, reduces swelling, and prevents recurrence, promoting healing and restoring normal function to the affected tooth and surrounding tissues.
Can Tooth Abscess Be Treated At Home?
No, tooth abscesses cannot be treated at home. Tooth abscesses must be treated with the help of a dental professional. A bacterial infection is the root cause of a severe dental condition known as a tooth abscess. Home remedies, such as heat and pain relievers, do not address the underlying infection. Professional dental treatment is needed to drain the abscess, treat the disease, and prevent further complications. Dentists have the expertise to manage and treat tooth abscesses safely, ensuring effective resolution and avoiding the spread of abscesses. Seeking prompt care helps with oral health.
Home remedies are available for temporary relief from pain and inflammation. Saltwater rinses, baking soda, and oregano essential oil help relieve discomfort. Saltwater rinses are affordable, while baking soda effectively removes plaque and promotes wound healing. Oregano essential oil has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, while cold compresses can reduce pain and swelling. Natural remedies for toothaches brought on by abscesses include fenugreek tea, clove, thyme, hydrogen peroxide, and oil pulling.
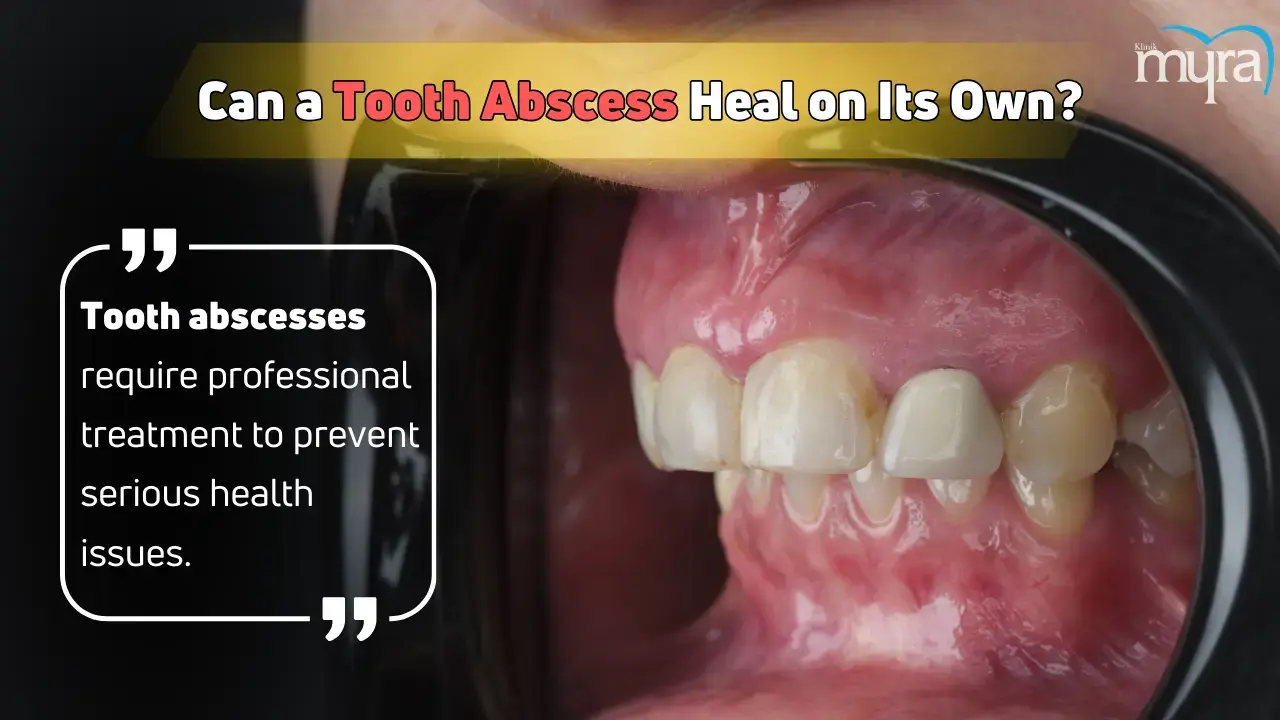
Will Tooth Abscess heal itself?
No, a tooth abscess will not heal itself. It is due to persistent infection, the risk of complications, damage to surrounding tissues, and the need for medical intervention. Bacterial growth and immune response contribute to the infection, which spreads to other areas and causes severe sepsis. Prolonged infection damages the tooth, necessitating extraction. The body heals naturally, but untreated tooth abscesses lead to serious health issues as the infection spreads and destroys surrounding tissues.
Professional dental treatment is necessary to remove the infection and prevent further dental problems. The underlying cause of the infection, such as gum disease or tooth decay, is not addressed, even if, in rare situations, the infection may drain on its own.
How do Tooth Abscess Affect Wisdom Tooth?
Tooth abscesses affect wisdom teeth by causing severe pain, swelling, and infection, necessitating extraction due to the difficulty in cleaning and the tendency to be partially erupted or impacted. Wisdom teeth, which are located at the back of the mouth, are difficult to clean, increasing the risk of bacterial infection. Causes of tooth abscess wisdom tooth include partial eruptions, gum flaps, and dental caries. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, redness, inflammation, pus discharge, difficulty opening the mouth, and fever.
Treatment for abscessed wisdom teeth includes antibiotics, drainage, extraction, pain management, and regular dental check-ups. Problem with wisdom tooth due to abscesses include infection spreading to adjacent teeth, the jawbone, other head and neck areas, tooth damage, cyst formation, and systemic infection.
What are the Researches about Tooth Abscess?
The research about tooth abscesses concerns the link between oral bacteria and brain abscesses and dental abscesses generated by root canal infection. The study by Jose F. Siqueira and Isabela N. Rocas reviews the aetiology, causes, and remedy of acute apical abscesses, a distinct type of dental abscess that results from an infection in the tooth's root canal. The study examines how host-related factors influence the development of the disease and discusses future directions in research, diagnosis, and therapeutic approaches.
New research led by Dr Raul Bescos and Dr Zoe Brookes has found that bacteria that cause oral infections contribute to patients developing life-threatening brain abscesses. The study, published in the Journal of Dentistry, examined the records of 87 patients with brain abscesses and used microbiological data from sampling and peripheral cultures. The results showed that 52 patients with no cause of the abscess had about three times the same oral bacteria in their samples. The patients carried higher counts of Streptococcus anginosus, a bacteria that leads to pharyngitis, bacteremia, and infections in internal organs such as the brain, lungs, and liver.
The findings suggest that the oral cavity is considered a source of infection in cases of brain abscesses where no clear cause has been identified. The research is part of ongoing research within the University's Oral Microbiome Research Group, which investigates the links between the oral microbiome and a range of cardiovascular and neurological conditions.
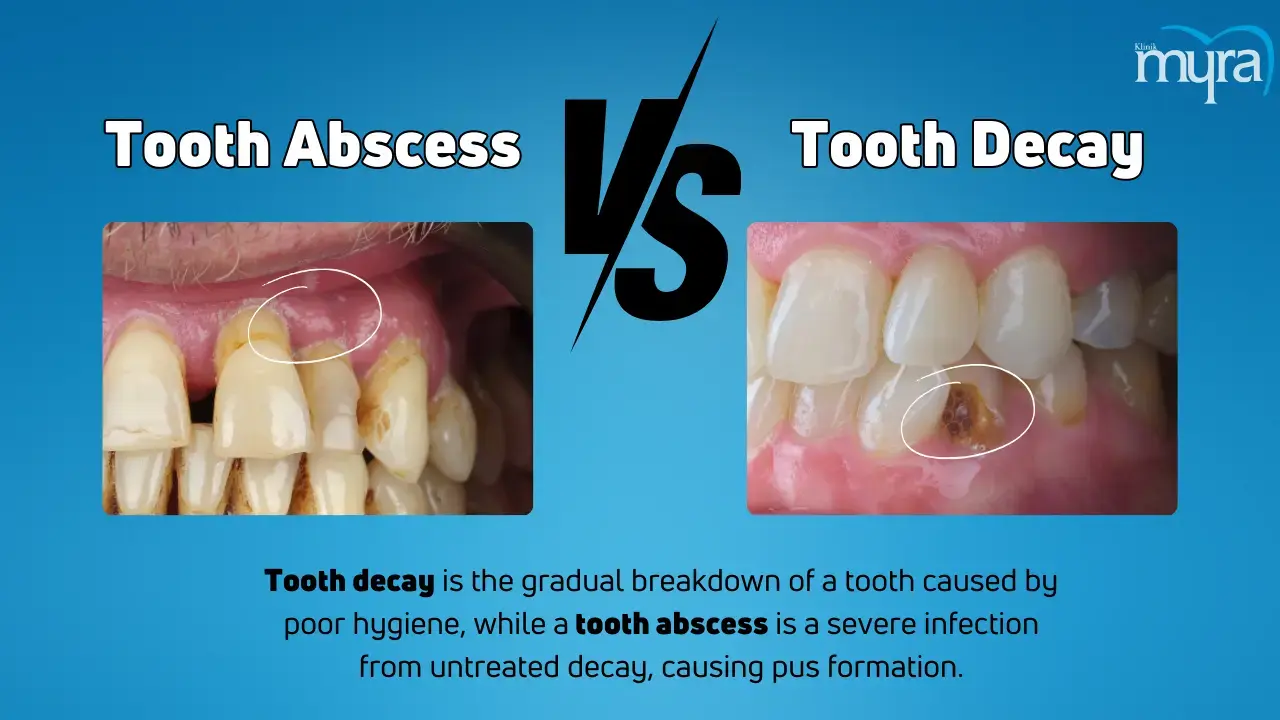
What are the Differences between Tooth Abscess and Tooth Decay?
The difference between tooth abscess and tooth decay is that tooth decay is a gradual breakdown of a tooth's structure, while tooth abscess is an infection that causes pus pockets. Tooth decay and tooth abscesses are related but have distinct causes. Poor oral hygiene and plaque buildup on teeth, which feed on sugars, are the leading causes of tooth decay and cavities. A tooth abscess is a severe condition caused by bacteria infiltrating the dental pulp due to untreated cavities, cracks, or gum disease.
Tooth decay treatment involves removing decayed tooth parts and filling them with restorative materials, while tooth abscessing requires more invasive procedures such as draining, root canaling, or extraction. Treatments for tooth decay problems vary depending on the severity of the condition. Restorative dental procedures, such as fluoride treatments and dental fillings, are used early, while advanced decay requires a crown. Root canal treatment is needed if decay reaches the pulp. Post-treatment, maintaining good oral hygiene, and regular dental check-ups are part of preventing recurrence.
Bacterial activity in the mouth causes tooth decay and abscesses, which destroy tooth structure. Tooth decay erodes tooth enamel, forming cavities that progress deeper. Untreated decay causes pain, discomfort, and serious oral health issues. Tooth decay and abscess conditions generate tooth loss, infection spread, and systemic health issues if left untreated. Keeping good oral hygiene techniques, such as brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, is part of managing dental conditions.