Osseointegration in Dental Implants has paved the way to more successful and longer lasting dental solutions. It has undeniably bestowed most dental patients an improved way of living. The use of osseointegration in Dental Implants has truly become a defining factor in the thriving market of dentistry nowadays. Osseointegration is defined as the process where the bone develops around a certain implant embedded in the body. It usually takes place during the course of a patient’s healing journey. Osseointegration is often incorporated in the installation of prosthesis or artificial body parts to replace the missing or defective portions of the body. The fusion of the bone and implant device produces added strength and stability to the specific area of the body in a faster way. It is the best advantage of incorporating osseointegration in the implantation of medical devices. One of the noted disadvantages of osseointegration is the fact that the location where the implant device is planted needs to be sanitised more frequently than usual. The same maintenance needs to be performed whether it is a dental implant or other prosthesis.
It usually amounts to £45831.20 for limb prosthesis. However, for dental implants, Osseointegration’s price is normally incorporated already into the total fee of the implant procedure. The average cost for the entire dental operation ranges from £454.79 to £42183.66. The application of osseointegration in Dental Implants have truly created a great shift in the dental care industry. It is expected to improve even more in the coming years.
What is Osseointegration?
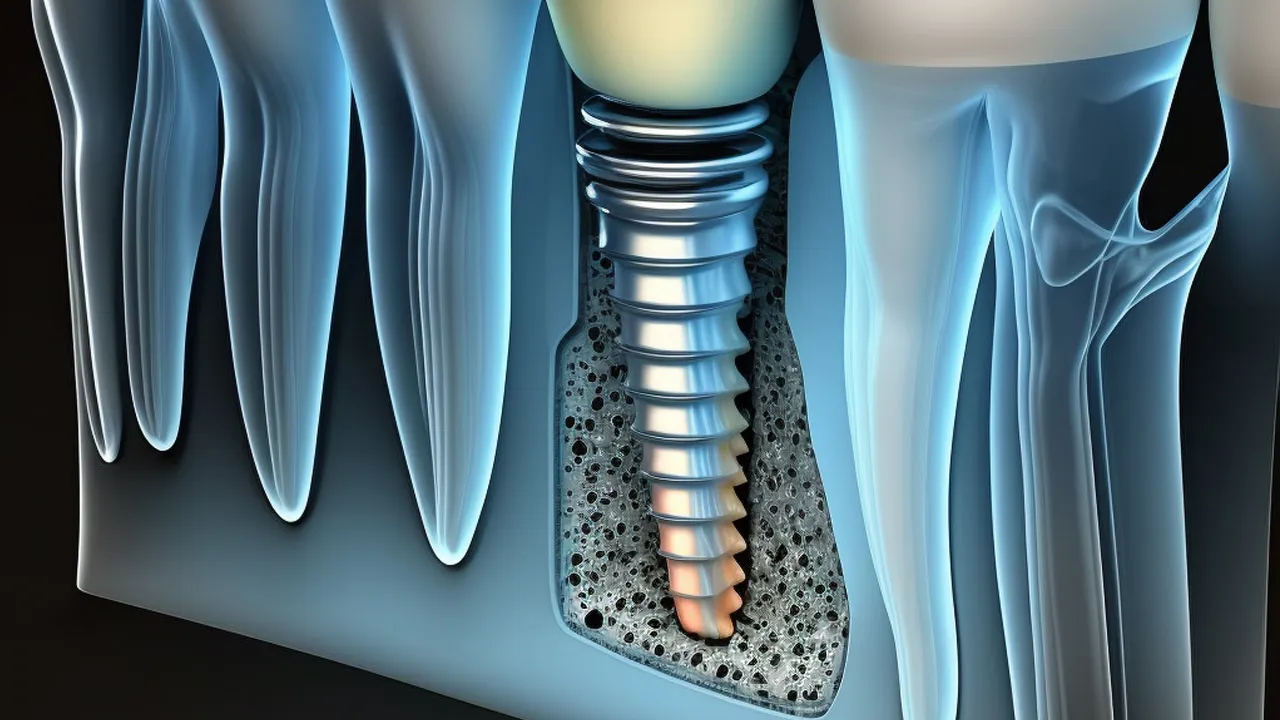
Osseointegration is defined as the unrestrained bond of the bone and the implant devices during the recuperation period. It is the phenomenon by which the inserted implant device builds a rigid anchoring to the bone as it grows around it, according to Merriam Webster Dictionary. The origin of the word osseointegration came from the Greek word “osteon” which means bone, and the Latin word “integrate” which means “to make whole again”. Osseointegration was initially noted in the year 1940 from the investigative studies conducted by Beaton and Davenport but it was not fully recognized at that time. It was Professor Per-Ingvar Branemark who first presented the phenomenon of the growing human bone cells in the presence of metallic implants in 1950. However, the idea was not given the name “osseointegration” yet. Branewark became fully convinced of his hypothesis in the year 1952 when he organised a research about the effect of blood circulation on the growth of bone mass in the midst of a titanium chamber. The subject he used was a rabbit whose bone was implanted with a titanium chamber. Branewark noticed that he is not able to pull out the titanium chamber easily anymore. He realised that the chamber had built a union with the bone. It was the time when Branewark named the phenomenon “osseointegration”. Osseointegration is used to pertain to a helpful method improving treatments for bone soreness from then on. Professor Branewark started developing dental implants with the use of osseointegration in the year 1965. The purpose of osseointegration has channelled to other fields of medical operations such as orthopaedic and spinal column. The working principle of osseointegration starts from bone calcification during the interaction of the bone and the implant device. The development of the bone tissues around the implant happens afterwards. The union of the bone and the implant finally takes place.
How does Osseointegration work in Dental Implants?
Osseointegration work in Dental Implants in a series of stages. Osseointegration occurs the moment the dental implant is embedded into the jawbone. Removal of the remaining tooth roots from the jawline must be done before conducting the implant insertion. There are some loose teeth which are not properly detached from the jawbone, especially those which are removed because of tooth decay.
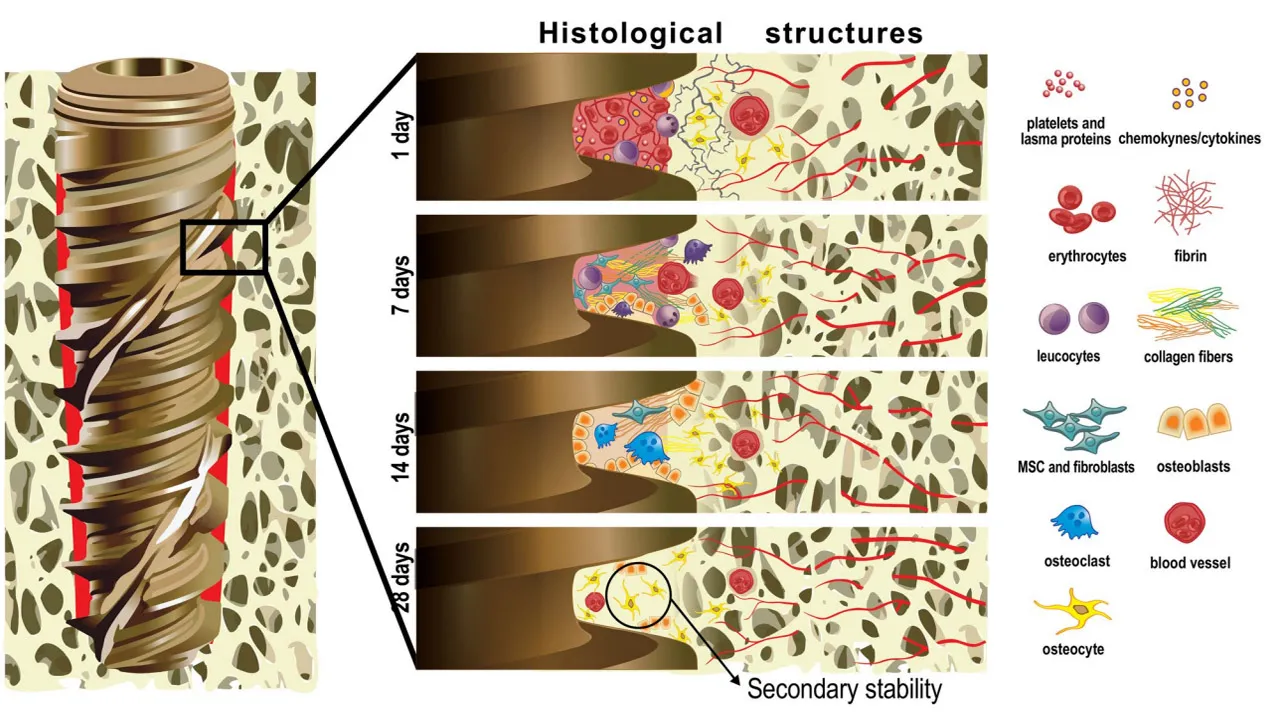
The process of osseointegration starts within two to three minutes after the dental implant is inserted into the operative location. It is called the Hemostasis stage. The Hemostasis Stage is when the blood forms a thick blanket around the dental implant which serves as the foundational layer for the healing process. The Inflammation stage takes place a few hours after the surgery. It is when the protecting cells in the gumline sweeps off surgical scraps and bacteria.
The micro blood vessels which are ruptured during the drilling stage are repaired and restored by the peri-vascular cells on the Inflammation stage. The third stage of Osseointegration is called the Proliferative stage. Proliferation is essential to bone regeneration. Proliferative stage is when the osteoblast cells are slowly brought out which happens days after the insertion of the implant device.
Osteoblast cells are responsible for the production of calcium phosphate and carbonate which are necessary to the development of new bone. The last stage for osseointegration is the Remodelling Stage. It usually takes place months or weeks after the surgery. It is when the osteocytes start the reformation of bone remodelling period.
The implanted dental device begins to unite with the bone and tissues.The abutment placement and crown attachment are later performed once the remodelling period is thru. The process of healing for Dental implant procedure comes in phases as well especially in endosteal implant cases. Once the dental implant is inserted into the patients’ jawline, the patient has to recuperate for two weeks. Another 3-6 months is required afterwards to allow the dental implant to be in unison with the bone. It is when osseointegration occurs.
The patient is expected to return to the clinic for the abutment placement after the 6 month healing period. The abutment placement is the phase where the abutment device is attached or connected to the dental posts. The gums must be opened again to be able to connect the abutment device, creating another wound in the mouth. It leads to another healing period which lasts within a few days up to two weeks.
Dental patients are advised to wait for another 6 months before the crown or artificial tooth is attached. Dental patients are able to use their implanted teeth like nothing happened. However, some dentists require their patients to wait for another 10 days before going back to their original diet or consuming food cravings.The process of osseointegration takes three to six months to complete.
Dental implants become part of the gums and jawbone through the process of osseointegration. Osseointegration is a medical phenomena which takes place during the healing period of the bones. It came from Greek and Latin words which literally means “a bone being whole again”. The dental implant embedded into the jawbone builds a union to the bone itself and the gumline.
The presence of titanium in the dental posts or screws triggers the osseointegration which enables the jawbone to grow and develop around it. Osseointegration goes through a series of phases which allows the microscopic particles in the jawbone and gumline to work together in repairing the ruptured site and in reforming the bone. Osseointegration is absolutely necessary to the success of Dental Implant because without a firm foundation to hold the implant devices, the whole process is expected to fail.
There is no successful dental implant procedure without osseointegration. Implant procedures without the application of osseointegration is a waste of money, time, and labour. Osseointegration is the one responsible for creating strong and stable roots for the artificial teeth. The bone and gum are not going to grow around the dental implant without osseointegration. It is not going to heal appropriately as well, making the dental implants unstable, weak, and short lived. Harmful effects are expected to take place in the jawbone and the gumline as well. The jawbone and gums are not going to heal appropriately thus inviting unwanted further damage to the nearby teeth and to the jawbone itself.
How much does Osseointegration cost in UK vs Turkey?
The cost of Osseointegration when incorporated in prosthetic extremities other than the teeth reaches to £45831.20 in UK. The price of osseointegration in dental devices, on the other hand , is already included in the total fee of a chosen procedure. There is no specific price listing which is dedicated for the osseointegration process in dental implant procedure. However, the average fee for a single dental implant procedure starts from £413.01 to £3769.51, osseointegration included. The average price of osseointegration operation in the lower limb amounts to £45655.51. There Is a separate price for those patients who need to undergo pre-implantation limb revision surgery whose cost soars to £41205.81. A yearly maintenance fee for osseointegrated prosthesis is charged differently after the major surgery. It costs £2199.72. The payment for Osseointegration is expected to soar depending on the difficulty of the patient’s needs, and other supplemental procedures required by the physician.
For international patients comparing dental implants in Turkey vs UK, the advantages of undergoing osseointegration for dental implants in Turkey are clear. Turkey’s world-class dental clinics utilize advanced techniques to ensure that the osseointegration process – where your implant securely fuses to the jawbone – is just as safe and successful as in the UK. The key difference is cost: dental implant treatments in Turkey come at a fraction of UK prices, often saving patients up to 70% without compromising on quality or safety. This means you receive the same top-tier implants and expert care, making Turkey an ideal choice for high-quality, affordable dental implant solutions.
What are the Benefits of Osseointegration in Dental Implants?
The benefits of Osseointegration in Dental Implants are truly relevant and promising. Some of these advantages include the union of the jawbone, the dental device, and the gum line altogether through the stimulus released by the titanium alloy from the implant devices. Osseointegration is at the heart of dental implantation. It is the root cause why dental grafts are thriving and attested to many dental patients. Osseointegration eventually provides added robustness and longevity to the dental graft. It helps to keep the wellness of the lower and upper arch up at the same time. The osseointegration process produces a sturdy and stable foundation for the dental devices. However, the most relevant advantage that osseointegration brings in Dental Implants is the fact that it allows the jawbone to develop around the dental device creating sturdy and durable foundational roots for the improvised teeth. The osseointegration process brings a lot more Benefits of Dental Implants to dental patients.
What are the Risks of Osseointegration?
The risks of osseointegration are important things that every dental patient must know about. There are noted complications during the course of osseointegration, although the procedure itself is unharmful. Three of the main risks involved in the process of osseointegration include infection, periprosthetic fracture, and aseptic loosening.
Infection is expected to occur in the superficial and intensive parts of the surgical area. Superficial infection involves the topmost layer of the skin and the subcutaneous tissues where the bacteria are promulgating. Intensive or deep seated infection effectuates beyond the subcutaneous tissues of the surgical area. The bacteria promulgates near the bone and the implant.
Studies show that patients who have been embedded with implants or prosthetics in the limbs or some other parts of the body other than the teeth experienced deep bone infection called osteomyelitis. It usually occurs 10 years after the surgery which has been encountered by 20% of the prosthetic patients. Periprosthetic fracture is another risk experienced by implant patients. It pertains to the damaged bones around the prosthetic itself. It usually happens during the process of inserting the implant into the bone or even during the healing period.
The bone around the implant gets very sensitive and unstable the moment the surgery is done making it more susceptible to fracture. The same phenomenon is expected to occur for implants inserted in the jawbone area. Another recorded risk of osseointegration is aseptic loosening. It is a condition where the bone and the implant fails to bond properly, even with the aid of osseointegration. It is usually experienced in orthopaedic operations. Patients who experience it are believed to have incompatibility factors towards the process of osseointegration. Dental patients are anticipated to experience aseptic loosening if they possess incompatible elements in their body.
The risks of osseointegration in dental implants is categorised into two. The first category pertains to the surgical complications of osseointegration. There are three to name a few of the surgical or operative risks of osseointegration in dental implants. These risks include neurosensory disturbance, blood clotting, and mandibular bone damage. Neurosensory disturbance or disorder occurs when neurosensory nerves are being touched unintentionally and unhealthily through surgery, tumour, or radiation.
The procedure for dental implantation and osseointegration are capable of hurting the neurosensory nerves during the process. Dental patients are anticipated to feel dental pain and change of taste when these neurosensory nerves are disturbed.
Another noted complication that patients are able to experience during osseointegration is hematoma or blood clotting. Blood clotting is actually a good indication of a healthy osseointegration. The effect of blood clot in the gums is a reverse of how it appears in the mouth. The production of blood clot after the dental implant has been inserted to the jawbone serves as a protective barrier for the bone nerve endings. Blood clotting stops excessive bleeding in the mouth.
Mandibular bone damage is another complication brought by osseointegration. Mandibular bone or jaw bone damage is anticipated to be experienced after the surgery or even during the procedure. It is often caused by weakened mandibles or loss of blood supply within the surgical area. The risk of osseointegration in terms of mechanical aspect include implant breakage, denture retention issues, and conflicting prosthesis fractures.
How long is the Process of Osseointegration?
The process of Osseointegration starts after the insertion of the dental implant deep down the patient’s jawbone. The wound accumulated during the insertion of the dental implant takes ample time to heal. The laceration is anticipated to heal in a matter of two to three weeks for most cases. Osseointegration begins when the laceration in the gumline is already sealed up. It usually takes three to six months for the whole osseointegration process to be completed.
The osseointegration process comprises four phases namely, the hemostasis phase, the inflammation phase, the proliferation phase, and the remodelling phase. These phases are discussed thoroughly above. The jawbone and dental implant are anticipated to build strong connections throughout the completion of these phases. The healing journey of dental implants appears to be longer and complicated than the traditional dental treatments but it provides long lasting results.
The jawbone becomes more stable and the dental roots are made stronger for the crowns because of osseointegration. The three to six month osseointegration period is not a waste of time but instead, an invested time for a better lifestyle in the future.
The next scenario after the completion of the osseointegration process, is the placement of the abutment device. The abutment device is a piece of titanium post where the crown or artificial teeth is being attached. The installation of an abutment device doesn't take so much time in the process. However, another laceration is required in the gumline to locate the opening of the inserted screw-like dental implant.
The abutment device is attached to the screw-like posts and the crown is placed at the top of it afterwards. The dental patients are advised to wait for 2 weeks to heal the wound again. Another six months must be allocated for the artificial tooth as an abutment device to have a firm position in the jawline. They are allowed to utilise their implanted teeth for eating purposes after the said six month recuperation period.
Is the Process of Osseointegration painful?
Yes, the process of osseointegration is anticipated to be painful. Pain is inevitable during osseointegration because the mouth is still adjusting with the new dental implant. The bone growing beneath the gums produces friction that causes discomfort in the jawline. However, the level of pain that the dental patients are going to feel depends on the tolerance that they personally hold.
Osseointegration is anticipated to be less painful for some patients but is excruciating for others. However, no patient is going to feel soreness during the surgery because anaesthetic drugs are injected right at the operative site. Discomfort is expected to be noticed a few days after the initial placement of dental implants when the power of anaesthetic drugs slowly diminishes. Pain is anticipated to heighten during the abutment placement because another laceration must be created.
The laceration leads to a much more sensitive gums making them more receptive to many things even to small movements. The installation of the crown or the artificial teeth to the abutment device produces less or no pain at all.
What is the successful rate of Osseointegration?
The successful rate of Osseointegration in dental implants continues to escalate over the years. An overall high rate of 97.6% is recorded for the efficacy of osseointegration in the utilisation of dental implants, according to Pubmed. A specific success rate is calculated for osseointegration in the maxilla which is 98.8 %, while it is 98.2% in the mandible. The administration of Osseointegration on other bones in the body such as the face notch an efficacy score of more than 95% as well.
A recently conducted study shows how dependable osseointegration is. The study presented two osseointegration procedures conducted on two different locations namely, the sterile surgery which is conducted in an operating room following intensive sterile rules, and the clean surgery which took place in a clinic room following critical rules. Both surgeries achieved a high success rate regardless of the location or the standard being followed during the procedure. It is a clear indication that osseointegration is a working wonder.
Osseointegration is the reason why dental implant treatment is efficient for most dental patients. Without the employment of osseointegration in dental devices, the success rate for implant procedures is going to crash. However, there are a lot of factors which contribute to the success and failure of osseointegration in dental implants. Some of these things include, the quality of the patient’s bone and second the lifestyle that a patient has. It is a great contributing factor for patients to submit to their dentists and follow the post surgery guidelines presented.
What does Osseointegration help in Dental Implants?
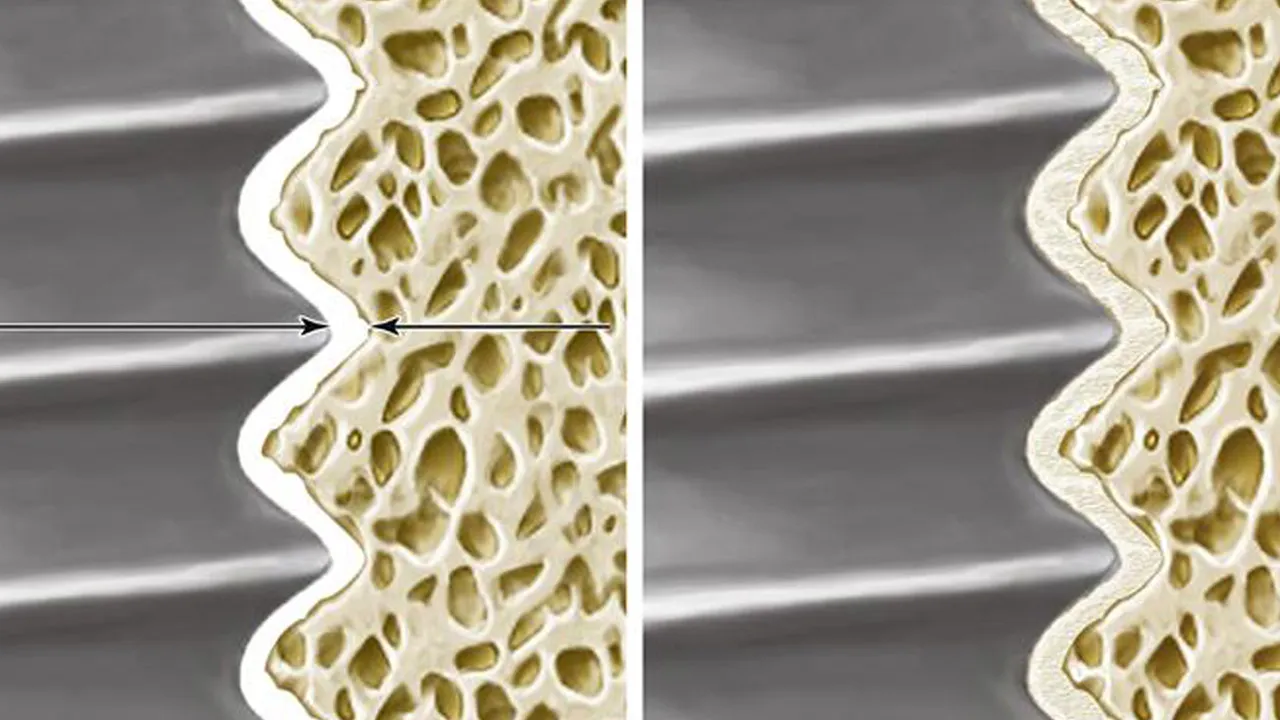
The process of Osseointegration helps in Dental Implants in a way that it strengthens the foundation of the dental roots. The bone tissues in the jaw area are able to grow and develop freely because of osseointegration despite the damage caused from drilling into the bone. Osseointegration makes it easier and faster for the connective tissues and nerves in the jawbone to repair themselves and to integrate once again.
Osseointegration allows the bone tissue to move and connect with other tissues even in the midst of a dental implant embedded beneath. The dental implants are not considered a hindrance to bone growth, instead it acts as a stimulus to bone development because it is made up of titanium alloy which is known to be a compatible element to the bone.
Osseointegration is a biological method used specifically in the skeletal component of the body where the natural bone is able to develop around an implanted device. The phenomena creates a stronger and more stable condition for the particular area of the body. Osseointegration is initially used for dental purposes but as the decades go by, science and technology brought it to the limbs, extremities and even in the face. The effectiveness of osseointegration in dental implantation is tested by a number of studies around the globe.
One of the studies about the usefulness of osseointegration was recorded in the early 90’s. The research made use of thirty two individuals who had 40 single-tooth missing, as its subject. These patients were implanted with 40 implants and were provided with regular maintenance service for almost 7 years. The dental implants remain intact, functioning well and looks stable upon checking. The results prove the efficacy of osseointegration.
What are the factors that affect Osseointegration?
Listed below are the factors that affect Osseointegration.
- Materials Used in the Implant. The materials used in the implant is an important factor that affects osseointegration. The dental implant must be made up of elements that are compatible with the bone components. Titanium is one of the natural elements in the world that is closely compatible with the human bone which most dental implants are made up of. The biocompatibility of titanium to the human bone leads dental implants to have a high success rate. It provides a great help for the development of the bone tissues and the connection of nerves by collaborating with osteocytes in the jawbone. Osteocytes perform a vital role in the establishment of osseointegration. Osseointegration is impossible to occur without compatible materials in the implant device. Dental implants therefore, need to be titanium based in order to effectively establish osseointegration.
- The Machining Condition. The machining condition refers to the manner that the titanium surface in the dental implants are being formed and presented.It is through Machining that Titanium Oxide films are created. These films are later formed through the process of anodization. The titanium films are being cleaned after anodization and are brought to the surface treatment process where its thickness and coarseness are assessed and set to a standard quality.The titanium filma are actually the surface that is able to make contact with the human body, and not the titanium metal itself. The surfaces of these titanium films covering the dental implants must be fashioned to a quality which allows cells to grow around it. There are two types of implant surfaces which are commonly used in titanium plates namely, the smooth surface and grooved surface. Bone cells opt to attach along the parallel grooves of a grooved film. These bone cells later form the osteocytes and osteoblasts the moment their numbers increase, creating a parallel formation in the film. The smooth surface film on the other hand, allows osteoblasts to proliferate over large areas, creating a rectangular formation. Researchers infer that osteoblasts build poorer attachments to smooth surfaced films compared to the grooved ones. The process of machining dictates the surface quality of the dental devices.
- The Type of Bone. The type of bone where the implant is placed is another essential factor to the process of osseointegration. The preference for the surface of titanium films is dependent on the type of bone where the implant is going to be attached. There are 4 types from which bones are categorised. These categories include D1, D2, D3 and D4. The D1 bones are thick and heavy cortical bones and trabecular bones. These types of bones require more caution during the preparation to avoid overheating. Dental implants to be used for D1 bones must at most have the length of 10mm. Another category of bone are the D2 bones. The D2 bones have a lower rate of density for cortical bone and vascularized trabecular bone. D2 bones are the type of bones that contain a lot of blood compared to D1 bones. The surface of the implant device is able to build better exposure with these blood which creates a good stability at the start of the process. D2 bones are compatible with implants which are 12mm long. It is required to keep the bones in contact with the surface of the implant by 50%. Another type of bone is called D3 bone. D3 bones are inferior to D2 bones in terms of density and mechanical power. The cortical and trabecular qualities that these bones have are poor making it brittle and susceptible to breakage. It appears that D3 bones offer a deficient anchorage to the implant. The last type of bones are the D4 bones. These bones are narrow and hold a low mechanical power. They consist of a slender cortical bone and a poorly mineralized trabecula. D4 bones are more fragile than D3 bones. Initial implant anchorage with D4 bones requires intricate operative procedure to be able to establish a successful anchorage at the beginning of osseointegration.
- The Surgical Method or Technique. The process of osseointegration is affected by the surgical technique used during the procedure. It is one of the factors that influence the firmness of the implant at the beginning of the osseointegration process. The type of surgical technique applied in the osseointegration has the ability to lengthen or shorten the healing period of the bones and body tissues around the implant. Altering the surgical technique shortens the recuperation period, along with modified design and adjusted titanium implant surfaces. The previous methods for the insertion of dental implants is complicated and extensive. A lot of bone tissues are affected and several drills are needed to install a dental implant during the early years of implant discovery. Several surgical methods have been developed for dental implants through the years to provide better stability while generating less damage to the jawbone and gums. One of the operative methods created to address the problem is called the “undersized drilling technique”. It is an operative method which uses an entity called osteotome spreader to squeeze the bone tissue obliquely. The undersized drilling method enhances the density of the bone by compressing it laterally. It is known to generate higher rates for the implantation of torques which improves the solidity of the dental implants in the bone. The said technique allows the bone fragments to be evenly dispersed in the surface of the implant as well. The levelled dispersion of bone particles activates an expedite healing of the bones around the implant and builds up the remodelling phase of osseointegration. Most manufacturers of dental implants recommend the implementation of undersized drilling technique for implant insertion. However, there are further studies conducted to improve the efficiency of the said surgical technique.
- Design of the Prosthesis. The design of prosthesis is another essential factor in the process of osseointegration. The design of the implant is better referred to as the shape of the implant dentistry. It influences the analysis for surface implants and creates a relevant impact to osseointegration. The design or shape of the implant or prosthesis is composed of the following factors: the measurement of the implant, the shape, the type of thread used, the height of fillets of thread, the thread inclination, the thread modulation and the type of connection for the implant prosthesis. The criteria for the measurement of the implants includes length, diameter and thickness. The shape of dental implants is either barrel-like, cylindrical, conical or a combination of these shapes. The type of threads used in the implants is another important element to the design of the prosthesis. The threads are either triangular, square, trapezoidal, rounded, or microthread. Another element under design is the connection type of the implant. The connection type is either external hexagon, internal hexagon, cone morse, or star grip. However, there is no standard design for dental implants yet, in spite of the influence that it brings to osseointegration. The most preferred implant design is the cylindrical screw threaded implant. Its compression ability is relatively higher than standard cylindrical threads. It has the capability to suppress compression rate on the bone and strengthens the foremost stability of the implant at the same time. Nevertheless, cylindrical screw thread implants are not appropriate for every dental dental case, in spite of its wonderful features. The previous design of the dental implants in the early stages of implant discovery comprises seven pieces. These parts include the initial implant, intermediate implant, intermediate screw, abutment, abutment screw, bolt retainer, and prosthesis. However, as the years passed, more and more clinical experiences have led the way to the advancement of implants. It is proven that the more components a dental implant has, the rate of potential damage is high as well. The current components of dental implants nowadays consist of the implant, the abutment, the abutment screw fixation and the prosthetic crown. There are occasions during the process of osseointegration that suggest the improvement of implants’ design, in spite of the wonders they are already making. There are instances when the other components of the implant device fail to provide stability during the first year of use, specifically the abutment screw. The problem gave birth to the creation of the different types of connection between the bone and the implant. Implants are built to have either the external or internal hexagon to answer the problem. It is imposed that the connection type and the dimension of the implants must be relatively balanced to edify the stability of osseointegration. The design of dental implants are being improved every now and then to provide better osseointegration between the bone and the implant itself.
- Oral Hygiene. The last but not the least among the factors affecting osseointegration is oral hygiene. Oral hygiene has the final say when it comes to the success of osseointegration. Osseointegration is a regenerative phenomenon which takes place during the recuperation period of the jawbone. Applying oral hygiene during the course of the healing time ensures the comprehensive success of osseointegration. The process of osseointegration is not intervened by unprecedented issues if the dental patient is hygiene minded. It eventually leads to rapid recovery, fewer dental risks and higher success rate in the implant procedure as a whole. One of the dental complications of poor or mediocre oral hygiene is Gum disease. Gum disease is an infection in the mouth brought by oral bacteria. It causes more complications in the gums which spread to the teeth and the jawbone itself. The process of osseointegration is at stake once the jawbone is not in good shape, which leads to implant failure. Proper oral hygiene does not solely pertain to regular brushing and flossing of the teeth and gargling of the mouth. Oral hygiene includes consuming the right entities to protect the teeth and avoiding the harmful ones. Cigarette smoking and utilisation of tobacco products is absolutely prohibited to dental implant patients. It is because these practices cause a lot of dental complications in the mouth. Some of these practices include gum disease, tartar and plaque build up, loss of tooth, and serious destruction to the structure of the teeth. Good oral hygiene brings a great influence to the success of osseointegration. These are the Factors that Affect Success Of Dental Implant during the process of osseointegration.
What causes the failure of Osseointegration?
Listed below are the factors that cause the failure of Osseointegration.
- Infection. The most common factor which causes failure of Osseointegration is infection. Infection is defined as the process of infecting or the state of being infected, according to Oxford Dictionary. It is a phenomenon when different kinds of germs and other microorganisms enter a specific part of the body, develop, and spread into other areas. It is primarily caused by poor personal hygiene habits. Infection creates more health issues as it spreads throughout the body like fever, cough, colds, body weakness, irritation, fatigue, and many more. A strong immune system often protects the body from acquiring infection. It is known to fight off Infection and lessen the severity of the illnesses it brings. However, there are patients who have weak immune systems making them vulnerable to infection. People with poor immune systems often suffer the severe symptoms of infection. Infection that is acquired during the process of osseointegration plays a role in the failure of dental implants procedures. The success of osseointegration itself is put at great risk because of infection. Infection at the time of osseointegration normally starts at the gum area. It is because a laceration is created in the gum line before drilling into the jawbone. These lacerations or open wounds are often the entry point of germs and other microorganisms into the mouth. Dental infection results in various oral problems when the patient has poor oral health habits. These oral issues frequently lead to serious implant failure most of the time. Infection at the time of operation leads to gum swelling and bone deterioration. A condition called Peri-implantitis is expected to occur when an infection is present in the surgical site. Peri-implantitis is the inflammation of the conjoining tissues around the dental implant leading to a successive deterioration of the bone holding up the implant. The dental implant needs to be detached from the patient’s jawbone, although it is able to be prevented. Other causes of infection aside from having bad oral habits include smoking, having fine gums, and diabetes.
- Tissue or nerve damage. The injury in the tissues and nerves in the mouth is one of the reasons why osseointegration fails. The tissues, particularly the nerves around the dental implant are exposed to damage once the dental implant is installed. Patients are expected to feel a striking sensation in most parts of the face like the tongue, gums, lips, chin, or cheeks when the implant has a slight distance from the nerve endings. It often leads to removal of the dental implant, but sometimes another healing period. Damage in the oral tissues and nerves close to the dental implant are generally created by malpractice. Dental patients are advised to make sure that the professional officiating the surgery is licensed and is certified to perform the implant procedure.
- Material placement. Material placement pertains to the gradual installation of the components of the dental implant. The placement of the components of dental implants involves two stages, as proposed by Professor Branemark, the person behind Osseointegration. The initial phase is when the implant is drilled into the surgical cavity in the jawbone. The healing period starts after the initial placement of the implant. It is the period when osseointegration begins as well. Osseointegration along with the healing process must take three to six months to ensure that the bone, the implant, and other connective tissues are able to build strong bonds with one another, as proposed by Branemark. The patients are instructed to have a second minor operation which is included in the second phase of the implant procedure, once the first phase is completed. The second stage of the procedure is the placement of the prosthesis. Another placement method has been developed to reduce the healing time for each implant procedure which researchers call “Immediately loading”. Immediately loading is the method which allows dentist professionals to place the implants and the artificial teeth in one single operation. However, there are necessary steps to follow in order to effectively apply “Immediate loading”. Some factors like the biocompatibility of titanium implant, the surgical method, and the design of the implant must be altered to coincide with the operational requirements of “Immediate loading”. There are cases, unfortunately, where the said loading procedure is used inappropriately. Overloading of dental components became a problem for some dental patients. It happens when the dental professional chooses to place all the components of the dental implant right after the insertion of the dental posts. The posts are not given enough time to build sufficient connection with the bone and other tissues. Overloading causes several complications to the bone and to the implant itself. Some of these risks include loosening of dental screws, infection, inflammation, and radiolucency around the implant. Loosening of the dental screws is the first noticeable indication of implant overloading which requires an immediate response to avoid serious problems. Infection is another evidence for implant overloading which is quite dangerous. It is expected that more complications arise, once infection reaches the surgical site. Inflammation occurs next to infection. Radiolucency on the other hand is the result of overpreparation of the implant platform due to overheating during the implant procedure. Patients who experience radiolucency acquire lesions around the gums, gingival reddening, painful inflamed mucosa, and tracts relating to a fistula. Overloading of dental components and peri-implantitis are late implant failures which are often experienced after the insertion of a dental implant into the jawbone.
- Biocompatibility of Materials used. Biocompatibility is an important factor that is able to influence the failure of osseointegration. It is described as the ability of an entity to function with a suitable response in a particular matter. Biocompatibility means that a certain component or device has the same or identical attributes to the live host where it is going to be used. The biocompatibility of dental components used in an implant operation must be ensured before conducting one. Dental grafts are known to be made from titanium alloy which is perfectly adaptable with living bones. The biocompatibility of the titanium in dental implants was initially evinced in a century old research facilitated by Professor Branemark to a rabbit bone. Branemark is the man who discovered the existence and occurrence of osseointegration. There are things that affect the biocompatibility of certain components. These things comprise the chemical structure, the mechanical attributes, the electrical charges, and the surface features of the material. It is assessed through proper observation of the link uniting the implant and the bone. The biocompatibility of a certain material or device is reliant on the situation where it is applied. The intraocular lenses and dental devices for example, are known to have biocompatibility. However, it is impossible to utilise the lenses to the implants, and the implants to the lenses. The biocompatibility of specific components for specific areas are not applicable to other purposes. The biocompatibility of dental materials is therefore vital to the proceedings of osseointegration. It is the defining factor for which components are able to work harmoniously with the bones and other nearby tissues. The procedure of osseointegration is not attainable if the materials used do not contain compatible attributes to the host, which in dental implants’ case is the jawbone. The factors discussed above are the most common Causes of Dental Implant Failure. Dental graft patients’ are advised to take these things into consideration before and during an implant process. It is a way to be more prepared for the operation and to be able to achieve successful dental implant installation.
Is Osseointegration Dental Implants Expensive?
Yes, Osseointegration in Dental Implants are expected to be expensive. The reason behind it is that dental implants involve advanced techniques and use new-technology mediums. Osseointegration is a century-old phenomenon discovered in the early years of 1950. However, in spite of its antiquity a lot of developments have been made to edify and ameliorate the efficacy of osseointegration. More refined dental implant techniques, exquisite dental processes, high-tech devices had been created throughout the course of implant discovery and progression. These further developments have raised the price metre of osseointegration. Osseointegration is a process utilised in the field of dentistry which is inclusive to the total fee of a specific dental implant process. There is no separate costing for osseointegration when employed in dental implant operations. The average price of a single tooth implant ranges from £413.01 to £3769.51 where osseointegration is already incorporated in UK. It is expected that as the type of dental implant gets severe, the price relatively gets expensive as well. Osseointegration is anticipated to cost more in high-priced and intensive 9 different types of dental implant. The most exorbitant dental device recorded is the full-mouth dental implant which costs £2148.92 to £76136.10. Osseointegration for that kind of implant must have greater cost compared to simpler and cheaper dental implant installations.
However, Turkey offers a more cost-effective alternative, with implant prices ranging from £400 to £850. These lower costs for teeth implants in Turkey are attributed to competitive market dynamics, favorable economic conditions, and high-quality services delivered by skilled professionals.In Turkey, full-mouth dental implant procedures are substantially more affordable, often costing up to 70% less than in countries like the UK or the US. Despite the cost difference, patients receive high-quality care, leveraging the latest in dental technology and expertise, making Turkey a leading destination for full-mouth restorations.
Do Osseointegration in Dental Implants have a high success rate?
Yes, osseointegration on dental implants has a high success rate. The average efficacy rate of osseointegration in dental devices is more than 95%. There are several winning stories from patients who are undeniably satisfied with the outcome of their dental operations.These success stories are not attainable without the supplication of osseointegration in the graft process. Osseointegration is one of the top reasons why dental devices are effective, efficient and surviving. Dental implants are expected to fail without the administration of the process of osseointegration. Osseointegration is the method wherein the bone tissues and the dental implant are able to connect with one another beneath the gum surface creating a stronger foundation for the artificial teeth. The cost of osseointegration is already included in the total dental implant procedure cost. Standard dental implant processes like a single tooth implant cost from £2513.01 to £3769.51. The osseointegration cost of a more complex and intensive dental device is expected to be greater compared to simpler and cheaper dental implant installations, such as the full-mouth dental device operation which costs £21148.92 to £76136.10. When deciding about dental implant clinics between the UK and Turkey, factors such as budget, time availability, and desired level of convenience play a crucial role. Both countries offer excellent options, but Turkey has become a global leader for those seeking premium dental treatments at a fraction of the cost.
Is Osseointegration Common in Dental Implantation?
Yes, osseointegration is absolutely common in dental implantation. Osseointegration acts as the firm foundation for dental implantation to be successful. It is the reason why dental implant processes are successful. Osseointegration takes place during the recuperation period of the drilled jawbone. It helps the jawbone repair itself in a convenient way around the dental device.
The moment the bone and other connective tissues are able to bond in the midst of the dental device, the footing for the artificial teeth are made stronger and firmer. Thus creating a stable, durable, and long lasting dental device in the mouth. There is no separate costing for osseointegration when used in dental implant processes because it is already included in the total payment of the specific dental implant operation.
The average price of a single tooth implant where osseointegration is already included ranges from £2513.01 to £3769.51 in UK. The cost of Osseointegration is anticipated to get more expensive in extensive and complete types of dental grafts, just like the full-mouth dental implant which costs £21148.92 to £76136.10.
What is the difference between Osseointegration and Biointegration?
The difference between Osseointegration and Biointegration revolves around the specificity of the purpose that they hold. They are used in different areas in the medical field, although both terms indicate the integration of a medical material or device into a living tissue. Osseointegration is used primarily in dentistry. It is the process where the dental implant and the tissues around it are able to connect with another, creating a levelled and complete jawbone.
Biointegration on the other hand, is a general term used in various areas in the medical field. It refers to the integration of a medical apparatus with specific living tissues. Osseointegration is considered under the umbrella of biointegration. Biointegration involves medical devices such as dental implants, peacemakers, and other prosthetics. Moreover, the aim of Osseointegration and Biointegration boils down to the same concept that is to establish a durable and long lasting connection between a specific medical device and the living tissues of the host.





