Dental bonding is a cosmetic dentistry method involving tooth-colored resin application to one’s damaged tooth and then hardening the resin with the use of a laser or another source of light. The material is molded and polished to the point that it cannot be distinguished from real teeth in any way. Bonding is used in repairing fractured or cracked teeth as well as in altering the color of stained teeth or otherwise discolored. There are a few different varieties of dental bonding, the most common of which are direct, indirect, composite, and composite veneer bonding. The cost of dental bonding varies widely based on a variety of circumstances namely the individual’s location, the dentist they see, the number of teeth that need to be fixed, and so on. The amount of time required to recuperate is rather brief in most cases, and the process itself is easy.
What is Dental Bonding?
The process of dental bonding requires the use of a composite resin material that is cured with the use of a laser or another kind of light source. It allows the material to closely match the color of the patient's teeth. It is sculpted and polished after the resin has had time to cure, so that it matches the appearance of the rest of the patient's teeth. Many different approaches are used during the procedure, each of which comes with its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages.
Direct bonding, in which the composite resin material is deposited directly on the tooth and then molded into the appropriate form before it hardens, is the most common procedure. The whole process is completed in a single appointment at the clinic. It is the most convenient way, and it is customized to a broad range of circumstances, which makes it ideal for making speedy improvements and cosmetic alterations.
Another approach is called indirect bonding, and it is the one that dentists and orthodontists use when they need to do more extensive repairs or correct more severely crooked teeth. An imprint of the tooth is first taken during the treatment, and then the space is filled with composite resin. The mold is placed over the tooth after the composite material has been formed into a mold, and the composite is allowed to cure in place. The use of such a time-consuming approach is beneficial for larger restorations, including as dental inlays and onlays, as well as orthodontic treatment.
Another technique is called adhesive bonding, which is more often referred to as etch-and-rinse bonding. Tiny grooves in such process are etched into the surface of the tooth using an acid, then washed away, and finally filled with a bonding agent before composite resin is placed. Such kind of procedure strengthens the bond between the tooth and the composite resin, which is particularly beneficial for larger restorations as well as teeth that are subjected to strong biting or chewing pressures.
In conclusion, dental bonding is an essential procedure for many patients since it is able to treat a broad range of dental conditions, such as chipping, discolouration, and incorrect tooth shape. It is utilized as a dental restoration material both for aesthetic reasons, such as altering the color or form of teeth, and for restorative purposes, such as repairing teeth that have been damaged by illness or wear. In addition, bonding is used to cover up discoloration, repair worn or chipped teeth, fill tiny cavities, reduce gaps between teeth, modify the curve of teeth, and repair worn or chipped teeth.
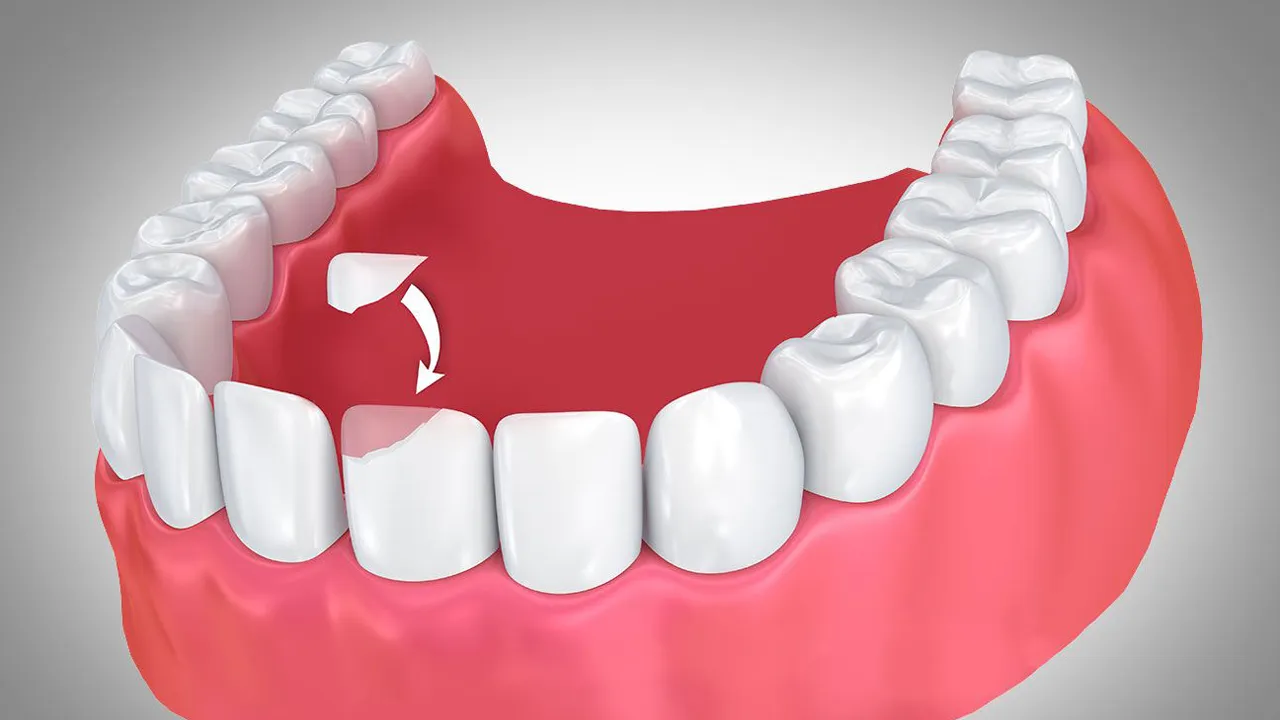
When is Dental Bonding needed?
Dental bonding is a method often done in order to correct a broad range of dental problems. It is a technique usually utilized in repairing damaged teeth in some way, such as chipped, cracked or broken teeth. Such is a therapy that is often recommended when teeth are damaged as a result of an accident or injury. The lost tooth structure is replaced with composite resin-made components which are then designed and hardened to form a smooth, natural-looking restoration that in turn restores the tooth’s function and appearance. Dental bonding is utilized to improve the look of teeth that have been chipped, discolored, or otherwise worn down. They make a person seem more attractive when they smile because they are color-matched to a person’s actual teeth. Additionally, it is used to build up teeth that have been damaged or rotted, as well as bridge gaps between teeth that have been created by hereditary factors or the loss of teeth. They are shaped and heated in a mold so that they fit comfortably in the interdental area.
What are the procedures of Dental Bonding?
Almost all bonding procedures are finished in a single dental appointment, taking between 30 and 60 minutes per tooth.
First, the dentist needs to choose which tooth serves as the “working tooth” before the actual bonding treatment begins. Teeth are examined in detail, with factors including color, form, and size taken into account. The dentist usually uses x-rays to assess the health of the tooth and bone around it.
The dentist next roughens up the tooth’s surface and applies a conditioning solvent after cleaning it. It aids the bonding material to cling to the tooth more efficiently. The dental expert then puts the bonding material to the tooth using a little spatula or brush. The substance is solidified by a specific light after being molded and sculpted into the proper form.
The dentist carefully molds and polishes the teeth after the material has solidified, to create the desired appearance. The final stage is to examine the bite and make any final changes needed to ensure that the tooth operates properly.
What are the types of Dental Bonding?
The following are the several forms of dental bonding:
- Direct Dental Bonding: It is a procedure that rapidly and effectively repairs teeth that have been splintered or have decayed in only one office visit. It returns the teeth to their original appearance, shape, and color while restoring their function.
- Composite Dental Bonding: It is the method of putting tooth-colored fillings on an individual’s tooth. Such procedure is performed on one or many teeth.
- Composite Veneer Bonding: Such procedure modifies the size, color, and form of a client’s teeth. It does so by filling in gaps and adjusting the length of the teeth.
- Indirect Dental Bonding: It is a restorative therapy that repairs damaged or decayed teeth.

1. Direct Dental Bonding
Direct dental bonding is a method in which a tooth-colored composite resin material is directly applied to a tooth, molded, and then solidified utilizing a specific light. Such process takes place during direct dental bonding operation. It is a bonding form often utilized for the purpose of changing the shape of teeth in addition to repairing chips, fractures, gaps, and discoloration in the teeth.
The tooth-colored composite is applied to the tooth itself immediately during the process. A high-intensity light is afterwards utilized to solidify the composite resin after it has been molded into the appropriate form. The dentist next polishes and smoothens the teeth following the cleaning. The whole process only takes between thirty and sixty minutes to complete.
It is essential to keep up a high level of oral hygiene and to carefully adhere to the dentist’s postoperative care recommendations as in cases with any other kind of dental operation. Patients are cautioned to refrain from eating anything that requires them to bite or chew for the first twenty-four hours after the treatment. Furthermore, patients have to abstain from eating or drinking anything that potentially discolor the bonding substance for at least forty-eight hours following the treatment.
Direct dental bonding is distinguished from other kinds of bonding, such as porcelain veneers, by the use of composite resin material that is applied directly to the tooth. Veneers, on the other hand, are thin shells of porcelain that are custom-made to fit over the front surface of a tooth. The said distinction is what distinguishes direct dental bonding from other types of bonding. However, veneers are more costly than composite bonding material and they are typically believed to be more stain-resistant and more durable. Composite bonding materials, on the other hand, are used to repair minor chips, fractures, or gaps on tooth surfaces, while veneers are mostly employed for cosmetic reasons. It is still another distinction between the two.
2. Composite Dental Bonding
Composite dental bonding entails putting tooth-colored composite resin, molding it, and hardening it afterwards utilizing a specific light, to restore teeth issues. Quartz powder or fine glass is mixed with plastic resin to make such resin substance. It is utilized in fixing one’s teeth and improving its appeal. Veneers are no different than bonding regarding the components utilized. Conversely, composite veneers enclose the whole tooth, whilst composite dental bonding just encloses a tiny tooth section.
The technique is often used to modify the contour of teeth in addition to repairing chips, fractures, gaps, and discolored teeth. It is used to close spaces between teeth. The operation is often completed in a single appointment, it does not include any sort of invasive surgery, and it takes much less time when compared to other forms of dental restorations, such as dental crowns. It is necessary to prevent behaviors such as biting the fingernails, chewing on pencils, or using teeth to open packages because the bonding substance has a propensity to chip. These are all things that are avoided. Therefore, avoiding these habits is necessary in order to guarantee that the impact of the bonding lasts long.
3. Composite Veneer Bonding
Composite veneers are manufactured to order utilizing a composite resin that is bonded to the front surface of the tooth and then shaped and polished to the patient's specifications. Such procedure encloses the full surface of the tooth in contrast to composite bonding, which only covers a portion of the tooth. The only purpose of the said procedure is to enhance the appearance of the tooth by modifying its size, shape, and color. They are placed on natural teeth to enhance the look of teeth that have been damaged, have lost their natural color, have an uneven form, or are not correctly aligned. It is used by the dentist to modify the length of the teeth and to close spaces that exist between the teeth. Composite veneer bonding lasts for up to eight years before they need to be replaced if they are maintained properly.
The following stages are those that are generally included in the process. The tooth, together with any decay or damage, is first polished and then thoroughly cleaned. The surface of the tooth is then softly scratched to provide a rougher texture, which assists in the bonding material's ability to attach more effectively. After that, a tooth-colored composite resin substance is painted onto the tooth, and it is sculpted into the proper shape using dental instruments. The material afterwards is made more durable by being exposed to a certain light. The patient's tooth is trimmed and shaped by the dentist so that it blends in with the rest of the mouth's teeth. It is essential to complete the process in order to guarantee that the tooth that has been bonded seems natural and merges in seamlessly with the rest of the mouth's teeth. The surface of the tooth that has been bonded is then polished so that it is smooth and glossy.
The bonding of composite veneers is a reasonably easy and risk-free technique; nevertheless, there are certain measures that are followed to assure the best possible result. Some of these preventative measures include avoiding foods that are hard or sticky, not smoking and not drinking excessive amounts of alcohol, practicing proper oral hygiene, wearing a night guard if users grind the teeth at night, and going to the dentist for check ups on a regular basis.
4. Indirect Dental Bonding
The look of the patient's teeth is improved by the use of a dental technique known as indirect dental bonding. Such process involves the use of a prefabricated tooth-colored material, such as porcelain. The procedure is often performed on a tooth that has been significantly damaged or stained for too long.
The first step of the technique is called tooth preparation, and it consists of cleaning the teeth and removing any decay or damage from it. The tooth is then prepared to be used as a mold. An imprint of the tooth is obtained, which is then sent to a dental laboratory to be used in the creation of a restoration that is unique to the patient. The restoration that was designed specifically for it is then cemented to the tooth using dental cement, after the tooth has been prepped. The surface of the tooth that has been bonded is polished afterwards so that it is smooth and shiny.
A tooth that has been damaged or has decay is restored with indirect bonding; however, in contrast to direct bonding, such process takes two visits to the dentist. The afflicted tooth is cleaned and prepared by the dentist, and then impressions are taken. The imprints are sent to a dental laboratory so that a dental inlay, onlay, or filling is manufactured there. Composite resin is used in the production of indirect dental bonding. They are very robust and long-lasting because the lab workers cure the restorations in a high temperature environment.
How much does a Dental Bonding Cost?
The price of a dental bonding in Turkey varies anywhere from £63 to £486 per tooth on average without taking into account the possibility of dental insurance coverage. The price is greater or cheaper based on the dentist's degree of expertise as well as the location of the dental office in Turkey. A dental bonding process ranges in price based on a number of different aspects, such as the materials that are used, the areas of the body that are being repaired, and the degree of difficulty of the operation.
A dental bonding price in Turkey varies depending on a number of factors, including the materials used, the body parts being treated, the level of intricacy of the procedure, the patient's location, and whether or not they have dental insurance.
The cost of the bonding substance is variable and is determined by the kind of composite resin material that is being used. There are certain materials that are much more costly than others, which have an impact on the total cost of the process. Furthermore, the price of a dental bonding process changes based on the area of the body that has to be treated. The dental bonding cost at the back tooth is more than the cost of bonding at the front tooth, for example, since bonding a front tooth is believed to be less sophisticated than bonding a rear tooth. Additionally, the total cost of a dental bonding operation in Turkey fluctuates based on the degree of difficulty involved in the process. A case that entails reshaping or filling gaps, as well as treating several teeth, often costs more than a straightforward repair of a chip on the surface of the tooth, for example.
Coverage for bonding is often included in dental insurance policies; however, the amount of coverage provided by each plan varies, and deductibles or co-insurance are required. It is in one's best interest to verify with the insurance carrier to see whether or not bonding is covered and how much money is needed to be paid out of pocket. Lastly, the cost of dental bonding in Turkey varies not only depending on location but the amount of skill of the dentist doing the procedure. In general, the cost of dental operations is going to be greater in metropolitan locations compared to rural ones, and dentists who have more expertise are going to charge more for their services.
In general, the cost of dental operations is going to be greater in metropolitan locations compared to rural ones, and dentists who have more expertise are going to charge more for their services. For patients evaluating cosmetic procedures like bonding, it’s essential to compare overall affordability and quality through a detailed understanding of Dental Treatment Prices in Turkey.
How long does it take to Recover from Dental Bonding?
The amount of time needed for recovery after dental bonding surgery is normally rather brief, and the majority of patients report feeling very little pain in the aftermath of the treatment. The vast majority of individuals totally recovered within a week or two, and the majority of their sensitivity swiftly faded away. It takes a little bit more time for the sensitivity to go away, and some individuals continue to feel a little bit uncomfortable for many weeks in other instances.
The process of healing starts as soon as the treatment is finished, and the majority of patients are able to go back to their usual activities the very next day. The patient has some modest sensitivity to warmth or pressure for a few days following the surgery; however, these symptoms are typically treated with over-the-counter pain medication.
It is essential to refrain from biting into something that is particularly tough or chewy for the first twenty-four hours after the treatment to enable the bonding substance to completely solidify. Additionally, it is recommended that for at least the first 48 hours following the treatment, refrain from eating or drinking anything that potentially taints the bonding substance.
Composite bonding, although having a decent durability, is not as robust and resistant to wear as other restorative choices, and it has the tendency to get discolored, chipped, or de-bonded over the course of time. Maintaining the intended results and ensuring that the bonding lasts as long as possible requires excellent oral hygiene and regular dental examinations.
What are the benefits of Dental Bonding?
Dental bonding is a commonly utilized method for it has shown to be beneficial in enhancing both the aesthetic and teeth’s function. The following are some of the advantages of dental bonding:
Improving the teeth appeal: Dental bonding is utilized in modifying teeth’s contour as well as mend fractures, gaps, chips, and discoloration in one’s teeth. The procedure is utilized to close spaces between teeth. It helps generate a more appealing smile that seems more natural and enhances the overall teeth appearance.
Strengthening teeth: The process of dental bonding is used to repair and restore teeth’s structural integrity that is weakened due to injury or illness. Dental bonding helps prevent teeth from suffering more damage while improving the tooth's overall strength and stability, by repairing tooth’s chips, gaps, and cracks.
Preserving tooth structure: Dental bonding is considered a conservative treatment option since it maintains the patient’s original tooth structure to the greatest extent feasible. Other restorative solutions such as dental crowns or inlays, in comparison, need more tooth material to be removed prior to the insertion of the replacement.
Improving function: Dental bonding is utilized to rehabilitate teeth that have been broken or worn down, therefore enhancing their functionality and making it simpler to chew food and communicate verbally.
Cost-effective solution: Dental bonding is typically regarded to be a remedy for tooth repair that is both cost-effective and efficient, when compared to several alternative cosmetic or restorative choices.
Fast and easy: Dental bonding is a technique which only requires one visit to the dentist’s office and is notable for its speed, simplicity, and lack of invasiveness. The process takes between 30 and 60 minutes per tooth, in most cases.
What are the risks of Dental Bonding?
Dental bonding is a technique that is typically safe and has a minimal risk of complications, but just like any other dental operation, there is always the possibility of anything going wrong. The following are some of the possible dangers associated with dental bonding:
- Allergic reactions: The composite resin substance that is used in dental bonding has the tendency to cause an allergic response in certain people. Redness, itching, and swelling are some of the symptoms that accompany an allergic response.
- Staining: The dental bonding material has a propensity to get discolored over time, particularly if the patient smokes or eats substances that cause discoloration, like coffee, tea, or red wine. Maintaining proper oral hygiene and cleaning the teeth on a regular basis helps reduce the appearance of stains.
- Chipping or breaking: The dental bonding material shatters or breaks if the patient bites into hard or chewy foods, or if they apply undue force to the tooth.
- De-bonding: De-bonding occurs in very unusual circumstances when the bonding material does not attach to the tooth in the correct manner.
- Sensitivity: Some individuals report feeling somewhat sensitive to cold or pressure after the surgery, although it is normally temporary and goes away after a few days. The sensitivity lasts for many weeks after the first exposure, in some situations.
- Possible need for re-treatment: The dental bonding material deteriorates over time and either needs to be repaired or replaced.
It is essential to have a conversation with the dentist about any concerns about the process, including the medical history and any drugs that are currently used, prior to undertaking the operation. Dental bonding endures for many years if it is cared for properly; nevertheless, getting frequent checkups is essential to guarantee that the bonding remains as long as possible.
How long does Dental Bonding last?
The length of time that dental bonding lasts is contingent upon a number of elements, such as the kind of material that was used, the location of the bonding, the patient's oral hygiene and habits, and the level of expertise possessed by the dentist.
Bonding in dentistry is designed to endure for a number of years on average, although its longevity often ranges anywhere from three to seven years. Composite dental bonding, which is one of the most prevalent forms of bonding, has a lifespan that normally ranges anywhere from three to seven years before it requires repair or further maintenance. On the other hand, maintaining good oral hygiene and going in for regular checkups at the dentist assists to prolong the bonding's useful life.
What are the side effects of Dental Bonding?
Dental bonding, which is known as tooth bonding, is a technique in which a tooth-colored resin substance is applied to a tooth, molded, and then cured using a specific light. Some of the potential adverse consequences of dental bonding are as follows:
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures: A patient experiences sensitivity to extremes of temperature in the days after the operation because the bonding material is put to the tooth in liquid form during a dental bonding surgery and subsequently hardened using a specific light. The tooth is left somewhat dry and more porous than before during the process, both of which contribute to the tooth's increased sensitivity. The tooth continues to be sensitive after the process has been completed if the bonding material is put to a tooth that already had sensitivity before the operation.
- Tooth discoloration: There are a few potential causes for tooth discolouration in the aftermath of a dental bonding surgery. There are several probable causes, but one of them is that the bonding material does not exactly match the color of the tooth, which results in an obvious mismatch. Additionally, it occurs if an excessive amount of bonding material is used, which results in the tooth seeming darker and gives the impression that it is bulkier. Lastly, discoloration occurs if the operation is performed on a tooth that has already been discolored as a result of an underlying disease such as trauma, infection, or cavities in the tooth.
- Chipping or cracking of the bonded tooth: There is a greater risk of it shattering or chipping once the procedure is completed, if the tooth is not adequately prepared for the bonding operation. Additionally, it occurs if the bonding material is too thin and does not give the tooth sufficient support. Some of the other potential causes include insufficiently high-quality materials were utilized, the patient's behaviors contributed to the problem, and the tooth has already been injured before the treatment.
- Allergic reaction: Reactions of an allergic nature after a dental bonding surgery are uncommon, but they happen if the patient is allergic to any of the ingredients that were used in the bonding process.
Does Dental Bonding have long term side effects?
Dental bonding is a procedure that is considered to be low risk and reasonably safe, and it does not often result in any adverse long-term consequences. The treatment is often performed without severe problems occurring in the majority of patients.
It is important to note, however, that dental bonding is considered a cosmetic procedure and is not covered by insurance. It is due to the fact that it is more prone to wear and tear, chipping cracking, or discoloration over the course of time. Debonding occurs because the bonding material does not always cling to the tooth in the correct manner, as stated above. The bonding material has to be repaired or replaced entirely in these kinds of situations.
It is essential to have reasonable expectations about the result of the treatment, as well as to practice diligent oral hygiene and have frequent oral checkups, in order to guarantee that the bonding lasts for a significant amount of time. A person gets instructions from the dentist on how to properly care for bonded teeth.
Does dental bonding harm your teeth?
No, dental bonding is completely safe for teeth in most cases. However, it is essential to practice good dental hygiene and refrain from biting on anything too tough in order to avoid damaging the region where the teeth are bonded. The result is tooth damage if the bonding process is not carried out accurately or if the tooth itself is not adequately prepared. Additionally, it is essential to keep in mind that dental bonding is not a long-term solution and eventually needs replacement or maintenance work.
Is Dental Bonding the same as Dental Filling?
No, dental bonding and dental fillings process are distinct in any way. Dental bonding requires putting a tooth-colored composite resin directly to tooth; afterwards, the resin is set using a specialized light. The resin is sculpted and polished to appear like other teeth in one’s mouth. Dental bonding is a technique often utilized to repair chipped or fractured teeth as well as to enhance teeth’s appearance that are discolored or malformed. Meanwhile, the substance that is used in the process of filling a cavity in a tooth is referred to as a dental filling. Dental amalgam which is made of a combination of metals such as silver and mercury, is the most frequent kind of filling. Amalgam fillings are utilized in repairing teeth cavities. There is an option of getting composite fillings similar to teeth color and are constructed of tooth-colored plastic and glass.
Which one is preferable over the other is determined by the specific patient’s circumstances as well as the tooth that has to be treated. A lot of articles have stated specifics of dental bonding vs fillings. Dental bonding provides a more conservative treatment option since it maintains a greater number of the original tooth structure. However, dental fillings are a useful substitute particularly for bigger cavities that need to be filled. The precise nature of the problem with the tooth and the advice of the dentist both go into determining the optimal course of action.





